Voice assistants are everywhere now. People talk to their phones, ask questions of smart speakers, and expect apps to understand what they say. To build a conversational AI used to be really hard. You needed different services for speech recognition, processing what people mean, and making the computer talk back. Managing all the audio streams and making sure voices sound clear on different devices was a nightmare.
ZEGOCLOUD conversational AI solution makes this much simpler. You can add voice conversations to your app without dealing with complex audio processing or expensive backend systems. Your app can listen to users, understand what they want, and respond with natural-sounding speech.
This guide shows you how to build a conversational AI that actually works. Users will be able to have real voice conversations with your app.
Conversational AI Solutions Built by ZEGOCLOUD
ZEGOCLOUD treats AI agents like real participants in your app. Instead of building separate chatbots, you invite AI directly into voice calls, video rooms, or live streams. The AI joins as an active participant and talks with users in real-time.
Multiple people can speak with the same AI agent during group calls. The AI recognizes different voices, gives personalized responses, and even suggests topics to keep conversations flowing. It handles interruptions naturally and responds just like a human participant would.
This approach makes conversational AI feel more natural. Users don’t switch between talking to people and talking to bots. The AI agent participates in the same conversation using the same voice streams as everyone else in the room.

Prerequisites
Before building the conversational AI functionality, ensure you have these essential components:
- ZEGOCLOUD developer account and AI Agent service activation – Signup here.
- Node.js 18+ with npm for package management and development tooling.
- Valid AppID and ServerSecret credentials from ZEGOCLOUD admin console for authentication.
- Dashcope API key for AI responses, or any compatible LLM provider.
- Physical device with microphone access for voice testing, as browser simulators cannot provide reliable audio capabilities.
1. Project Setup
1.1 Understanding the System Architecture
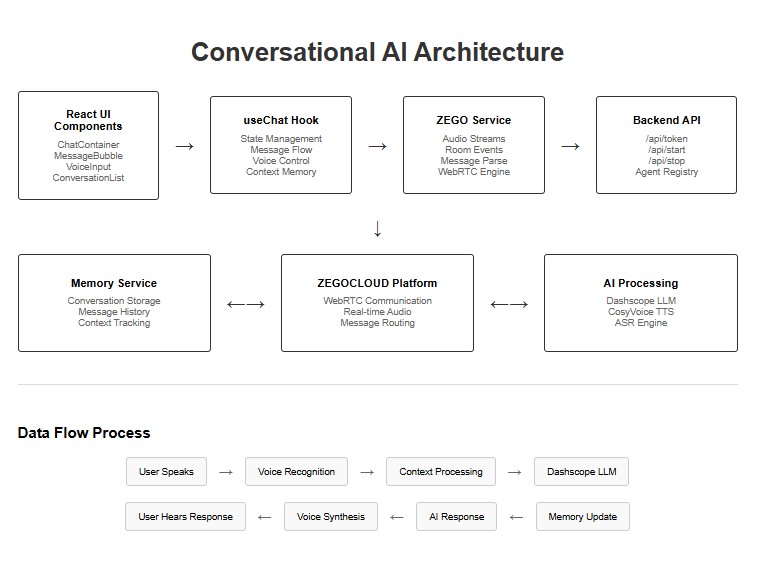
The backend serves four main purposes: generating authentication tokens, registering AI agents with voice characteristics, creating agent instances for conversations, and routing text messages.
The frontend coordinates ZEGOCLOUD’s WebRTC engine for audio streaming, state management for conversation flow, and local storage for persistence.
1.2 Dependencies and Environment Setup
Backend installation requires Express for API endpoints, crypto for ZEGOCLOUD authentication, and axios for API communication:
mkdir conversational-ai && cd conversational-ai
mkdir server client
cd server
npm init -y
npm install express cors dotenv axios typescript tsx
npm install --save-dev @types/express @types/cors @types/nodeFrontend setup uses Vite’s React template with ZEGOCLOUD’s WebRTC SDK:
cd ../client
npm create vite@latest . -- --template react-ts
npm install zego-express-engine-webrtc axios framer-motion lucide-react tailwindcss zodRename the .env.example file in the server directory to .env, then fill in the necessary values as instructed.
# server/.env
ZEGO_APP_ID=your_numeric_app_id
ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET=your_32_character_secret
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=your_dashscope_api_key
PORT=8080
# client/.env
VITE_ZEGO_APP_ID=your_numeric_app_id
VITE_ZEGO_SERVER=wss://webliveroom-api.zegocloud.com/ws
VITE_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8080This configuration enables the frontend to authenticate with ZEGOCLOUD rooms while the backend manages AI agent interactions through Dashscope’s language models.
2. Building the Voice Agent Server
2.1 ZEGOCLOUD API Authentication System
The server needs two authentication mechanisms: server-to-server API signatures for managing AI agents, and client tokens for room access. ZEGOCLOUD’s signature system uses MD5 hashing with specific parameter ordering.
// server/src/server.ts
import express, { Request, Response } from 'express'
import crypto from 'crypto'
import axios from 'axios'
import cors from 'cors'
import dotenv from 'dotenv'
import { createRequire } from 'module'
const require = createRequire(import.meta.url)
const { generateToken04 } = require('../zego-token.cjs')
dotenv.config()
const app = express()
app.use(express.json())
app.use(cors())
const CONFIG = {
ZEGO_APP_ID: process.env.ZEGO_APP_ID!,
ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET: process.env.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET!,
ZEGO_API_BASE_URL: 'https://aigc-aiagent-api.zegotech.cn/',
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY: process.env.DASHSCOPE_API_KEY || '',
PORT: parseInt(process.env.PORT || '8080', 10)
}
function generateZegoSignature(action: string) {
const timestamp = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000)
const nonce = crypto.randomBytes(8).toString('hex')
// ZEGOCLOUD requires specific parameter ordering for signature generation
const appId = CONFIG.ZEGO_APP_ID
const serverSecret = CONFIG.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET
const signString = appId + nonce + serverSecret + timestamp
const signature = crypto.createHash('md5').update(signString).digest('hex')
return {
Action: action,
AppId: appId,
SignatureNonce: nonce,
SignatureVersion: '2.0',
Timestamp: timestamp,
Signature: signature
}
}
async function makeZegoRequest(action: string, body: object = {}): Promise<any> {
const queryParams = generateZegoSignature(action)
const queryString = Object.entries(queryParams)
.map(([k, v]) => `${k}=${encodeURIComponent(String(v))}`)
.join('&')
const url = `${CONFIG.ZEGO_API_BASE_URL}?${queryString}`
const response = await axios.post(url, body, {
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
timeout: 30000
})
return response.data
}The signature generation follows ZEGOCLOUD’s exact specification – the parameter concatenation order matters for authentication.
2.2 AI Agent Registration and Configuration
Agent registration configures the AI’s personality, voice characteristics, and speech processing parameters. This happens once per server startup, creating a persistent agent that can join multiple conversations.
let REGISTERED_AGENT_ID: string | null = null
async function registerAgent(): Promise<string> {
if (REGISTERED_AGENT_ID) return REGISTERED_AGENT_ID
const agentId = `agent_${Date.now()}`
const agentConfig = {
AgentId: agentId,
Name: 'AI Assistant',
LLM: {
Url: 'https://dashscope-intl.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1/chat/completions',
ApiKey: CONFIG.DASHSCOPE_API_KEY || 'zego_test',
Model: 'qwen-plus',
SystemPrompt: 'You are a helpful AI assistant. Be concise and friendly. Respond in the same language as the user. Keep responses under 100 words for better voice conversation flow.',
Temperature: 0.7,
TopP: 0.9,
Params: {
max_tokens: 200 // Shorter responses work better for voice conversations
}
},
TTS: {
Vendor: 'CosyVoice',
Params: {
app: {
api_key: 'zego_test' // ZEGOCLOUD provides test credentials
},
payload: {
model: 'cosyvoice-v2',
parameters: {
voice: 'longxiaochun_v2', // Natural-sounding Chinese voice
speed: 1.0,
volume: 0.8
}
}
},
FilterText: [
{
BeginCharacters: '(',
EndCharacters: ')'
},
{
BeginCharacters: '[',
EndCharacters: ']'
}
]
},
ASR: {
HotWord: 'ZEGOCLOUD|10,AI|8,Assistant|8,money|10,help|8',
// These parameters control conversation naturalness
VADSilenceSegmentation: 1500, // Wait 1.5 seconds of silence before processing
PauseInterval: 2000 // Concatenate speech within 2 seconds
}
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('RegisterAgent', agentConfig)
if (result.Code !== 0) {
throw new Error(`RegisterAgent failed: ${result.Code} ${result.Message}`)
}
REGISTERED_AGENT_ID = agentId
return agentId
}The TTS FilterText configuration removes parenthetical text and bracketed content from speech synthesis, preventing awkward voice artifacts. The ASR parameters are crucial for natural conversation – the 1.5-second silence threshold prevents cutting off users mid-thought.
2.3 Session Management and Room Integration
Session creation connects individual users with AI agent instances inside ZEGOCLOUD rooms. Each conversation gets its own room with unique user and agent identifiers.
app.post('/api/start', async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> => {
const { room_id, user_id, user_stream_id } = req.body
if (!room_id || !user_id) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'room_id and user_id required' })
return
}
// Ensure agent is registered before creating instances
const agentId = await registerAgent()
const userStreamId = user_stream_id || `${user_id}_stream`
const agentUserId = `agent_${room_id}`
const agentStreamId = `agent_stream_${room_id}`
const instanceConfig = {
AgentId: agentId,
UserId: user_id,
RTC: {
RoomId: room_id,
AgentUserId: agentUserId,
AgentStreamId: agentStreamId,
UserStreamId: userStreamId
},
MessageHistory: {
SyncMode: 1, // Sync conversation history with frontend
Messages: [],
WindowSize: 10 // Keep last 10 messages for context
},
CallbackConfig: {
ASRResult: 1, // Send voice transcription events
LLMResult: 1, // Send AI response events
Exception: 1, // Send error events
Interrupted: 1, // Send interruption events
UserSpeakAction: 1, // Send user speech start/stop events
AgentSpeakAction: 1 // Send AI speech start/stop events
},
AdvancedConfig: {
InterruptMode: 0 // Enable natural voice interruption
}
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('CreateAgentInstance', instanceConfig)
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message || 'Failed to create instance' })
return
}
res.json({
success: true,
agentInstanceId: result.Data?.AgentInstanceId,
agentUserId: agentUserId,
agentStreamId: agentStreamId,
userStreamId: userStreamId
})
})The callback configuration enables real-time communication between the AI agent and frontend. The interruption mode setting enables users to interrupt the AI mid-response, just like talking to a person.
2.4 Message Routing and Session Cleanup
Text message routing allows users to type instead of speaking, while maintaining the same conversation context:
app.post('/api/send-message', async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> => {
const { agent_instance_id, message } = req.body
if (!agent_instance_id || !message) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'agent_instance_id and message required' })
return
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('SendAgentInstanceLLM', {
AgentInstanceId: agent_instance_id,
Text: message,
AddQuestionToHistory: true, // Include user message in conversation context
AddAnswerToHistory: true // Include AI response in conversation context
})
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message || 'Failed to send message' })
return
}
res.json({ success: true })
})
app.get('/api/token', (req: Request, res: Response): void => {
const userId = req.query.user_id as string
const roomId = req.query.room_id as string
if (!userId) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'user_id required' })
return
}
const payload = {
room_id: roomId || '',
privilege: { 1: 1, 2: 1 }, // Login and publish privileges
stream_id_list: null
}
const token = generateToken04(
parseInt(CONFIG.ZEGO_APP_ID, 10),
userId,
CONFIG.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET,
3600, // 1 hour expiration
JSON.stringify(payload)
)
res.json({ token })
})
app.post('/api/stop', async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> => {
const { agent_instance_id } = req.body
const result = await makeZegoRequest('DeleteAgentInstance', {
AgentInstanceId: agent_instance_id
})
res.json({ success: true })
})The server maintains conversation context by adding both questions and answers to the AI agent’s history, enabling contextual responses that reference previous parts of the conversation.
Get the complete server code implementation.
3. ZEGOCLOUD WebRTC Integration
3.1 WebRTC Engine Setup and Audio Management
The frontend WebRTC integration manages real-time audio streaming between users and AI agents. We use a singleton service to prevent multiple engine instances, which would cause audio conflicts.
// client/src/services/zego.ts
import { ZegoExpressEngine } from 'zego-express-engine-webrtc'
import { config } from '../config'
import { agentAPI } from './api'
export class ZegoService {
private static instance: ZegoService
private zg: ZegoExpressEngine | null = null
private isInitialized = false
private currentRoomId: string | null = null
private currentUserId: string | null = null
private localStream: any = null
private audioElement: HTMLAudioElement | null = null
static getInstance(): ZegoService {
if (!ZegoService.instance) {
ZegoService.instance = new ZegoService()
}
return ZegoService.instance
}
async initialize(): Promise<void> {
if (this.isInitialized) return
this.zg = new ZegoExpressEngine(
parseInt(config.ZEGO_APP_ID),
config.ZEGO_SERVER
)
this.setupEventListeners()
this.setupAudioElement()
this.isInitialized = true
}
private setupAudioElement(): void {
// Create or reuse the audio element for AI agent playback
this.audioElement = document.getElementById('ai-audio-output') as HTMLAudioElement
if (!this.audioElement) {
this.audioElement = document.createElement('audio')
this.audioElement.id = 'ai-audio-output'
this.audioElement.autoplay = true
this.audioElement.controls = false
this.audioElement.style.display = 'none'
document.body.appendChild(this.audioElement)
}
this.audioElement.volume = 0.8
this.audioElement.muted = false
}3.2 Room Event Processing and Message Callbacks
ZEGOCLOUD sends conversation events through room message channels. The frontend processes different event types to update UI state and manage conversation flow.
private setupEventListeners(): void {
if (!this.zg) return
// Process room messages containing voice transcriptions and AI responses
this.zg.on('recvExperimentalAPI', (result: any) => {
const { method, content } = result
if (method === 'onRecvRoomChannelMessage') {
const message = JSON.parse(content.msgContent)
this.handleRoomMessage(message)
}
})
// Handle AI agent audio streams joining/leaving the room
this.zg.on('roomStreamUpdate', async (_roomID: string, updateType: string, streamList: any[]) => {
if (updateType === 'ADD' && streamList.length > 0) {
for (const stream of streamList) {
const userStreamId = this.currentUserId ? `${this.currentUserId}_stream` : null
// Skip the user's own stream to prevent audio feedback
if (userStreamId && stream.streamID === userStreamId) {
continue
}
// Connect AI agent audio stream to browser audio system
const mediaStream = await this.zg!.startPlayingStream(stream.streamID)
if (mediaStream) {
const remoteView = await this.zg!.createRemoteStreamView(mediaStream)
if (remoteView && this.audioElement) {
await remoteView.play(this.audioElement, {
enableAutoplayDialog: false,
muted: false
})
this.audioElement.muted = false
this.audioElement.volume = 0.8
}
}
}
} else if (updateType === 'DELETE') {
if (this.audioElement) {
this.audioElement.srcObject = null
}
}
})
}
private messageCallback: ((message: any) => void) | null = null
private handleRoomMessage(message: any): void {
if (this.messageCallback) {
this.messageCallback(message)
}
}
onRoomMessage(callback: (message: any) => void): void {
this.messageCallback = callback
}The stream update handler includes fallback audio connection logic because different browsers handle WebRTC audio differently.
3.3 Room Joining and User Stream Management
Room joining coordinates authentication, stream creation, and message reception setup:
async joinRoom(roomId: string, userId: string): Promise<boolean> {
if (!this.zg) return false
if (this.currentRoomId === roomId && this.currentUserId === userId) {
return true
}
// Leave previous room if exists
if (this.currentRoomId) {
await this.leaveRoom()
}
this.currentRoomId = roomId
this.currentUserId = userId
// Get authentication token from backend
const { token } = await agentAPI.getToken(userId)
// Join the ZEGOCLOUD room
await this.zg.loginRoom(roomId, token, {
userID: userId,
userName: userId
})
// Enable room message reception for AI agent communication
this.zg.callExperimentalAPI({
method: 'onRecvRoomChannelMessage',
params: {}
})
// Create and publish user audio stream
const localStream = await this.zg.createZegoStream({
camera: {
video: false, // Voice-only conversation
audio: true
}
})
if (localStream) {
this.localStream = localStream
const streamId = `${userId}_stream`
await this.zg.startPublishingStream(streamId, localStream, {
enableAutoSwitchVideoCodec: true // Optimize for voice
})
return true
} else {
throw new Error('Failed to create local stream')
}
}
async enableMicrophone(enabled: boolean): Promise<boolean> {
if (!this.zg || !this.localStream) return false
// Control the audio track directly
if (this.localStream.getAudioTracks) {
const audioTrack = this.localStream.getAudioTracks()[0]
if (audioTrack) {
audioTrack.enabled = enabled
return true
}
}
return false
}The room message reception setup is crucial for receiving AI agent communication. Without this, the frontend won’t receive voice transcriptions or AI response events. The complete Zego service code is here.
4. React Frontend Architecture
4.1 Configuration and Service Layer
The frontend uses Zod for environment validation and service abstractions for backend communication:
// client/src/config.ts
import { z } from 'zod'
const configSchema = z.object({
ZEGO_APP_ID: z.string().min(1, 'ZEGO App ID is required'),
ZEGO_SERVER: z.string().url('Valid ZEGO server URL required'),
API_BASE_URL: z.string().url('Valid API base URL required'),
})
const rawConfig = {
ZEGO_APP_ID: import.meta.env.VITE_ZEGO_APP_ID,
ZEGO_SERVER: import.meta.env.VITE_ZEGO_SERVER,
API_BASE_URL: import.meta.env.VITE_API_BASE_URL,
}
export const config = configSchema.parse(rawConfig)The API service abstracts backend communication with comprehensive error handling:
// client/src/services/api.ts
import axios from 'axios'
import { config } from '../config'
const api = axios.create({
baseURL: config.API_BASE_URL,
timeout: 30000,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
})
export const agentAPI = {
async startSession(roomId: string, userId: string) {
const requestData = {
room_id: roomId,
user_id: userId,
user_stream_id: `${userId}_stream`,
}
const response = await api.post('/api/start', requestData)
if (!response.data?.success) {
throw new Error(response.data?.error || 'Session start failed')
}
return { agentInstanceId: response.data.agentInstanceId }
},
async sendMessage(agentInstanceId: string, message: string) {
const requestData = {
agent_instance_id: agentInstanceId,
message: message.trim(),
}
const response = await api.post('/api/send-message', requestData)
if (!response.data?.success) {
throw new Error(response.data?.error || 'Message send failed')
}
},
async getToken(userId: string) {
const response = await api.get(`/api/token?user_id=${encodeURIComponent(userId)}`)
if (!response.data?.token) {
throw new Error('No token returned')
}
return { token: response.data.token }
}
}4.2 Local Conversation Memory Service
The memory service handles conversation persistence using localStorage with conversation metadata management:
// client/src/services/memory.ts
class MemoryService {
private static instance: MemoryService
private conversations: Map<string, ConversationMemory> = new Map()
static getInstance(): MemoryService {
if (!MemoryService.instance) {
MemoryService.instance = new MemoryService()
}
return MemoryService.instance
}
constructor() {
this.loadFromStorage()
}
private loadFromStorage(): void {
const stored = localStorage.getItem('ai_conversations')
if (stored) {
const conversations = JSON.parse(stored)
conversations.forEach(conv => {
this.conversations.set(conv.id, conv)
})
}
}
private saveToStorage(): void {
const conversations = Array.from(this.conversations.values())
localStorage.setItem('ai_conversations', JSON.stringify(conversations))
}
createOrGetConversation(id?: string) {
const conversationId = id || this.generateConversationId()
if (this.conversations.has(conversationId)) {
return this.conversations.get(conversationId)!
}
const newConversation = {
id: conversationId,
title: 'New Conversation',
messages: [],
createdAt: Date.now(),
updatedAt: Date.now(),
metadata: {
totalMessages: 0,
lastAIResponse: '',
topics: []
}
}
this.conversations.set(conversationId, newConversation)
this.saveToStorage()
return newConversation
}
addMessage(conversationId: string, message) {
const conversation = this.conversations.get(conversationId)
if (!conversation) return
// Update existing message or add new one
const existingIndex = conversation.messages.findIndex(m => m.id === message.id)
if (existingIndex >= 0) {
conversation.messages[existingIndex] = message
} else {
conversation.messages.push(message)
}
// Update conversation metadata
conversation.updatedAt = Date.now()
conversation.metadata.totalMessages = conversation.messages.length
if (message.sender === 'ai') {
conversation.metadata.lastAIResponse = message.content
}
// Set conversation title from first user message
if (conversation.messages.length === 1 && message.sender === 'user') {
conversation.title = message.content.slice(0, 50) + (message.content.length > 50 ? '...' : '')
}
this.saveToStorage()
}
getAllConversations() {
return Array.from(this.conversations.values())
.sort((a, b) => b.updatedAt - a.updatedAt)
}
private generateConversationId(): string {
return `conv_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9)}`
}
}
export const memoryService = MemoryService.getInstance()5. Message Streaming System
5.1 State Management with useChat Hook
The useChat hook coordinates all conversation state using useReducer for predictable updates across multiple async operations. This is the most complex part of the frontend, managing ZEGOCLOUD events, API calls, and local storage simultaneously.
// client/src/hooks/useChat.ts
import { useCallback, useRef, useEffect, useReducer } from 'react'
import { ZegoService } from '../services/zego'
import { agentAPI } from '../services/api'
import { memoryService } from '../services/memory'
const initialState = {
messages: [],
session: null,
conversation: null,
isLoading: false,
isConnected: false,
isRecording: false,
currentTranscript: '',
agentStatus: 'idle',
error: null
}
function chatReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'SET_MESSAGES':
return { ...state, messages: action.payload }
case 'ADD_MESSAGE':
// Prevent duplicate messages during streaming
const exists = state.messages.some(m => m.id === action.payload.id)
if (exists) {
return {
...state,
messages: state.messages.map(m =>
m.id === action.payload.id ? action.payload : m
)
}
}
return { ...state, messages: [...state.messages, action.payload] }
case 'UPDATE_MESSAGE':
return {
...state,
messages: state.messages.map(m =>
m.id === action.payload.id ? { ...m, ...action.payload.updates } : m
)
}
case 'SET_SESSION':
return { ...state, session: action.payload }
case 'SET_CONNECTED':
return { ...state, isConnected: action.payload }
case 'SET_RECORDING':
return { ...state, isRecording: action.payload }
case 'SET_TRANSCRIPT':
return { ...state, currentTranscript: action.payload }
case 'SET_AGENT_STATUS':
return { ...state, agentStatus: action.payload }
default:
return state
}
}
export const useChat = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(chatReducer, initialState)
const zegoService = useRef(ZegoService.getInstance())
const processedMessageIds = useRef(new Set())
const currentConversationRef = useRef(null)
const streamingMessages = useRef(new Map())5.2 Real-time Message Processing
The message handling system processes different event types from ZEGOCLOUD, managing voice transcription and streaming AI responses:
const setupMessageHandlers = useCallback((conv) => {
const handleRoomMessage = (data) => {
const { Cmd, Data: msgData } = data
// Ensure message belongs to current conversation
if (currentConversationRef.current !== conv.id) {
return
}
if (Cmd === 3) {
// Voice transcription from user speech
const { Text: transcript, EndFlag, MessageId } = msgData
if (transcript && transcript.trim()) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT', payload: transcript })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'listening' })
if (EndFlag) {
// Complete voice transcription - create user message
const messageId = MessageId || `voice_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
const userMessage = {
id: messageId,
content: transcript.trim(),
sender: 'user',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'voice',
transcript: transcript.trim()
}
addMessageSafely(userMessage, conv.id)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT', payload: '' })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'thinking' })
}
}
} else if (Cmd === 4) {
// AI response streaming - build response chunk by chunk
const { Text: content, MessageId, EndFlag } = msgData
if (!content || !MessageId) return
if (EndFlag) {
// Final chunk - complete the streaming message
const currentStreaming = streamingMessages.current.get(MessageId) || ''
const finalContent = currentStreaming + content
dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE_MESSAGE', payload: {
id: MessageId,
updates: {
content: finalContent,
isStreaming: false
}
}})
streamingMessages.current.delete(MessageId)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
// Save completed message to persistent storage
const finalMessage = {
id: MessageId,
content: finalContent,
sender: 'ai',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text'
}
memoryService.addMessage(conv.id, finalMessage)
} else {
// Intermediate chunk - build up the response
const currentStreaming = streamingMessages.current.get(MessageId) || ''
const updatedContent = currentStreaming + content
streamingMessages.current.set(MessageId, updatedContent)
if (!processedMessageIds.current.has(MessageId)) {
// Create new streaming message
const streamingMessage = {
id: MessageId,
content: updatedContent,
sender: 'ai',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text',
isStreaming: true
}
processedMessageIds.current.add(MessageId)
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_MESSAGE', payload: streamingMessage })
} else {
// Update existing streaming message
dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE_MESSAGE', payload: {
id: MessageId,
updates: { content: updatedContent, isStreaming: true }
}})
}
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'speaking' })
}
}
}
zegoService.current.onRoomMessage(handleRoomMessage)
}, [])
const addMessageSafely = useCallback((message, conversationId) => {
if (processedMessageIds.current.has(message.id)) {
return
}
processedMessageIds.current.add(message.id)
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_MESSAGE', payload: message })
memoryService.addMessage(conversationId, message)
}, [])5.3 Session Management and User Interactions
Session management coordinates the complex startup sequence while user interaction functions handle voice recording and text messaging:
const startSession = useCallback(async (conversationId) => {
if (state.isLoading || state.isConnected) return false
dispatch({ type: 'SET_LOADING', payload: true })
const roomId = `room_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
const userId = `user_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
// Initialize ZEGO service
await zegoService.current.initialize()
// Join ZEGOCLOUD room
const joinResult = await zegoService.current.joinRoom(roomId, userId)
if (!joinResult) throw new Error('Failed to join ZEGO room')
// Start AI agent session
const result = await agentAPI.startSession(roomId, userId)
// Set up conversation memory
const conv = memoryService.createOrGetConversation(conversationId)
currentConversationRef.current = conv.id
const newSession = {
roomId,
userId,
agentInstanceId: result.agentInstanceId,
isActive: true,
conversationId: conv.id
}
dispatch({ type: 'SET_SESSION', payload: newSession })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_CONNECTED', payload: true })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_MESSAGES', payload: [...conv.messages] })
setupMessageHandlers(conv)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_LOADING', payload: false })
return true
}, [state.isLoading, state.isConnected])
const sendTextMessage = useCallback(async (content) => {
if (!state.session?.agentInstanceId || !state.conversation) return
const trimmedContent = content.trim()
if (!trimmedContent) return
const messageId = `text_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
const userMessage = {
id: messageId,
content: trimmedContent,
sender: 'user',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text'
}
addMessageSafely(userMessage, state.conversation.id)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'thinking' })
await agentAPI.sendMessage(state.session.agentInstanceId, trimmedContent)
}, [state.session, state.conversation, addMessageSafely])
const toggleVoiceRecording = useCallback(async () => {
if (!state.isConnected) return
if (state.isRecording) {
await zegoService.current.enableMicrophone(false)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_RECORDING', payload: false })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
} else {
const success = await zegoService.current.enableMicrophone(true)
if (success) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_RECORDING', payload: true })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'listening' })
}
}
}, [state.isConnected, state.isRecording])
return {
...state,
startSession,
sendTextMessage,
toggleVoiceRecording
}
}The hook returns all state and functions needed by React components, abstracting away the complex coordination between ZEGOCLOUD, backend APIs, and local storage.
6. Running and Testing
6.1 Clone the Repository
To test, clone the sample Zego Agent repository with the complete implementation and install the packages with:
npm install6.2 Run the Server
Start the backend server with hot reloading:
cd server
npm run devLaunch the frontend development server:
cd client
npm run devThe application opens at http://localhost:5173. The backend health endpoint at http://localhost:8080/health shows service status and configuration validation.
Run a Demo
If you open the frontend, you’ll see an interface like the one shown below. You can click on “Start Chat.”
Conclusion
That’s it! You’ve successfully built a complete conversational AI application using ZEGOCLOUD’s real-time communication platform. The system handles voice recognition, AI response generation, and natural conversation flow with persistent memory across sessions.
The application treats AI agents as real participants in voice calls, enabling natural interruption and real-time responses. Users can seamlessly switch between text and voice input while maintaining conversation context.
The modular architecture makes it easy to extend functionality and customize the experience for specific use cases. Your conversational AI system now provides professional-grade voice communication with the intelligence and responsiveness users expect from modern AI applications.
FAQ
Q1. What technologies are required to build a conversational AI?
You typically need natural language processing (NLP/LLM), automatic speech recognition (ASR), text-to-speech (TTS), and real-time communication (RTC) technologies. Together, they create a seamless loop for listening, understanding, and responding.
Q2. How do I integrate conversational AI into existing apps or platforms?
Most providers offer SDKs and APIs that support cross-platform integration (iOS, Android, Web). A well-documented, all-in-one SDK can significantly speed up development.
Q3. What are the main use cases of conversational AI?
Typical use cases include customer service bots, AI voice assistants, live streaming interactions, in-game NPCs, virtual classrooms, healthcare assistants, and enterprise collaboration tools.
Q4. How do I choose the right conversational AI provider?
Evaluate providers based on latency performance, global coverage, ease of integration, scalability, security standards, cost transparency, and proven case studies.
Let’s Build APP Together
Start building with real-time video, voice & chat SDK for apps today!










