Build an AI Voice Agent can seem harder than it looks. Many developers spend weeks combining speech recognition, natural language processing, and voice synthesis just to make basic voice features work. Each service comes with its own authentication steps, audio handling challenges, and hours of debugging, which quickly makes the process overwhelming.
Instead of dealing with all that complexity, imagine deploying a production-ready AI voice agent that understands speech, processes requests intelligently, and responds with natural, human-like voices in just minutes.
ZEGOCLOUD conversational AI provides a unified platform that manages the entire voice pipeline for you. There is no need for audio engineering, service orchestration, or infrastructure maintenance. With simple APIs, your application can turn voice input into intelligent, real-time responses.
This tutorial will guide you through the process. By the end, you will have built an AI voice agent that feels natural to interact with, delivers contextual replies instantly, and enhances user experiences across different scenarios.
How to Build an AI-Powered Voice Agent in 10 Minutes
ZEGOCLOUD built voice agents on top of their proven communication platform. The same technology that powers millions of voice calls now includes AI agents with speech recognition, language processing, and voice synthesis built right in.
This means you get years of audio optimization and network reliability that already work in production. Instead of experimental voice AI services, you’re using enterprise-grade communication tools with intelligent integrations now.
Your voice agent runs on established WebRTC protocols, tested audio codecs, and streaming technology that handles critical business communications worldwide. You get AI conversation capabilities through a foundation that already works reliably at scale.

Prerequisites
Before building your AI voice agent, ensure you have these components ready:
- ZEGOCLOUD developer account with valid AppID and ServerSecret – Sign up
- Any compatible LLM API key for intelligent conversation processing and contextual response generation.
- Node.js 18+ installed locally with npm for package management and development servers.
- Testing environment with microphone access since voice agents require real audio hardware capabilities.
- Basic familiarity with React hooks and Express.js patterns for following the implementation steps.
1. Project Setup and Configuration
Before we proceed with the setup, the diagram below shows how the parts of the voice agent we’re building connects:
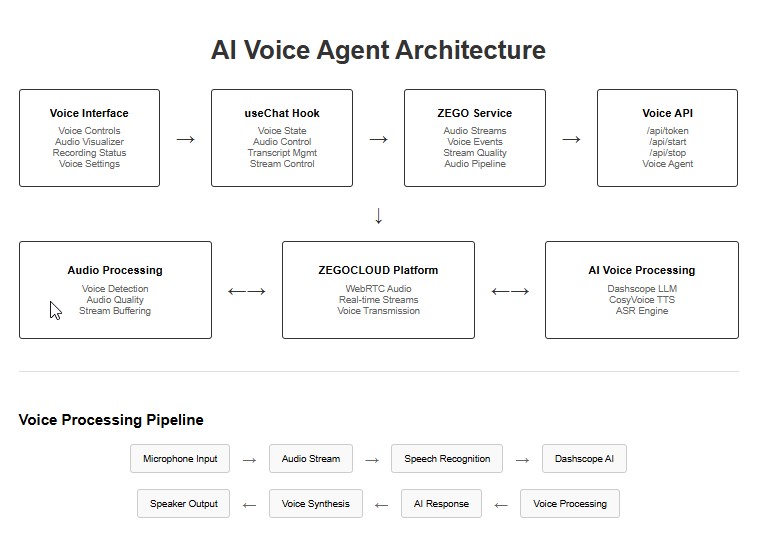
Now, create the project structure for your voice agent:
mkdir ai-voice-agent
cd ai-voice-agent
mkdir server clientInstall backend dependencies for voice agent processing:
cd server
npm init -y
npm install express cors dotenv axios typescript tsx
npm install --save-dev @types/express @types/cors @types/nodeRename the .env.example file in the server directory to .env, then fill in the necessary values as instructed.
ZEGO_APP_ID=your_zego_app_id
ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET=your_zego_server_secret
ZEGO_API_BASE_URL=https://aigc-aiagent-api.zegotech.cn
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=your_dashscope_api_key
PORT=80802. Voice Agent Server Implementation
2.1 Authentication System
Generate ZEGOCLOUD authentication tokens for voice sessions:
app.get('/api/token', (req: Request, res: Response): void => {
try {
const userId = req.query.user_id as string
const roomId = req.query.room_id as string
if (!userId) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'user_id required' })
return
}
const payload = {
room_id: roomId || '',
privilege: { 1: 1, 2: 1 }, // Login and publish permissions
stream_id_list: null
}
const token = generateToken04(
parseInt(CONFIG.ZEGO_APP_ID, 10),
userId,
CONFIG.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET,
3600,
JSON.stringify(payload)
)
res.json({ token })
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: 'Failed to generate token' })
}
})2.2 Voice Agent Registration
Configure the AI agent with voice-specific capabilities including speech recognition, text-to-speech, and conversation parameters:
async function registerAgent(): Promise<string> {
if (REGISTERED_AGENT_ID) return REGISTERED_AGENT_ID
const agentId = `agent_${Date.now()}`
const agentConfig = {
AgentId: agentId,
Name: 'AI Assistant',
LLM: {
Url: 'https://dashscope-intl.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1/chat/completions',
ApiKey: CONFIG.DASHSCOPE_API_KEY || 'zego_test',
Model: 'qwen-plus',
SystemPrompt: 'You are a helpful AI assistant. Be concise and friendly. Respond in the same language as the user. Keep responses under 100 words for better voice conversation flow.',
Temperature: 0.7,
TopP: 0.9,
Params: {
max_tokens: 200
}
},
TTS: {
Vendor: 'CosyVoice',
Params: {
app: {
api_key:'zego_test'
},
payload: {
model: 'cosyvoice-v2',
parameters: {
voice: 'longxiaochun_v2', // Natural Chinese voice
speed: 1.0,
volume: 0.8
}
}
},
FilterText: [
{
BeginCharacters: '(',
EndCharacters: ')'
},
{
BeginCharacters: '[',
EndCharacters: ']'
}
]
},
ASR: {
HotWord: 'ZEGOCLOUD|10,AI|8,Assistant|8,money|10,help|8',
VADSilenceSegmentation: 1500, // Wait 1.5 seconds before processing speech
PauseInterval: 2000 // Concatenate speech within 2 seconds
}
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('RegisterAgent', agentConfig)
if (result.Code !== 0) {
throw new Error(`RegisterAgent failed: ${result.Code} ${result.Message}`)
}
REGISTERED_AGENT_ID = agentId
console.log('Agent registered:', agentId)
return agentId
}The ASR configuration is crucial for voice agents – VADSilenceSegmentation prevents cutting off users mid-sentence, while PauseInterval handles natural speech patterns.
2.3 Voice Session Management
Create voice agent instances that handle real-time audio streams and voice processing:
app.post('/api/start', async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> => {
try {
const { room_id, user_id, user_stream_id } = req.body
if (!room_id || !user_id) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'room_id and user_id required' })
return
}
const agentId = await registerAgent()
const userStreamId = user_stream_id || `${user_id}_stream`
const agentUserId = `agent_${room_id}`
const agentStreamId = `agent_stream_${room_id}`
const instanceConfig = {
AgentId: agentId,
UserId: user_id,
RTC: {
RoomId: room_id,
AgentUserId: agentUserId,
AgentStreamId: agentStreamId,
UserStreamId: userStreamId
},
MessageHistory: {
SyncMode: 1,
Messages: [],
WindowSize: 10
},
CallbackConfig: {
ASRResult: 1, // Voice transcription events
LLMResult: 1, // AI response events
Exception: 1, // Error handling
Interrupted: 1, // Voice interruption support
UserSpeakAction: 1, // User speech start/stop
AgentSpeakAction: 1 // AI speech start/stop
},
AdvancedConfig: {
InterruptMode: 0 // Enable natural voice interruption
}
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('CreateAgentInstance', instanceConfig)
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message || 'Failed to create instance' })
return
}
res.json({
success: true,
agentInstanceId: result.Data?.AgentInstanceId,
agentUserId: agentUserId,
agentStreamId: agentStreamId,
userStreamId: userStreamId
})
} catch (error: any) {
console.error('Start error:', error)
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message || 'Internal error' })
}
})2.4 Session Cleanup
Properly terminate voice agent instances and release audio resources:
app.post('/api/stop', async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> => {
try {
const { agent_instance_id } = req.body
if (!agent_instance_id) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'agent_instance_id required' })
return
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('DeleteAgentInstance', {
AgentInstanceId: agent_instance_id
})
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message || 'Failed to delete instance' })
return
}
res.json({ success: true })
} catch (error: any) {
console.error('Stop error:', error)
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message || 'Internal error' })
}
})The complete server code is here.
3. Frontend Voice Interface
Set up the React client for voice interaction:
cd ../client
npm create vite@latest . -- --template react-ts
npm install zego-express-engine-webrtc axios framer-motion lucide-react tailwindcss zodEnvironment configuration:
VITE_ZEGO_APP_ID=your_zego_app_id
VITE_ZEGO_SERVER=wss://webliveroom-api.zegocloud.com/ws
VITE_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:80804. ZEGOCLOUD Voice Integration
4.1 Audio Stream Management
The core workflow: Initialize Engine → Setup Audio → Join Room → Handle Voice Events → Process Responses
export class ZegoService {
private static instance: ZegoService
private zg: ZegoExpressEngine | null = null
private audioElement: HTMLAudioElement | null = null
private currentRoomId: string | null = null
private currentUserId: string | null = null
private localStream: any = null
private setupAudioElement(): void {
// Create dedicated audio element for AI voice output
this.audioElement = document.getElementById('ai-audio-output') as HTMLAudioElement
if (!this.audioElement) {
this.audioElement = document.createElement('audio')
this.audioElement.id = 'ai-audio-output'
this.audioElement.autoplay = true
this.audioElement.controls = false
this.audioElement.style.display = 'none'
document.body.appendChild(this.audioElement)
}
this.audioElement.volume = 0.8
this.audioElement.muted = false
// Audio event monitoring for voice agent debugging
this.audioElement.addEventListener('loadstart', () => {
console.log('🔊 AI voice loading started')
})
this.audioElement.addEventListener('canplay', () => {
console.log('🔊 AI voice ready to play')
})
this.audioElement.addEventListener('play', () => {
console.log('🔊 AI voice playback started')
})
}
4.2 Voice Message Processing
Handle real-time voice transcription and AI response streaming:
typescriptprivate setupEventListeners(): void {
if (!this.zg) return
// Process voice messages from ZEGOCLOUD AI agent
this.zg.on('recvExperimentalAPI', (result: any) => {
const { method, content } = result
if (method === 'onRecvRoomChannelMessage') {
try {
const message = JSON.parse(content.msgContent)
console.log('🎯 Voice message received:', message)
this.handleRoomMessage(message)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to parse voice message:', error)
}
}
})
// Monitor AI agent audio streams
this.zg.on('roomStreamUpdate', async (_roomID: string, updateType: string, streamList: any[]) => {
console.log('📡 Audio stream update:', updateType, streamList.length, 'streams')
if (updateType === 'ADD' && streamList.length > 0) {
for (const stream of streamList) {
const userStreamId = this.currentUserId ? `${this.currentUserId}_stream` : null
// Skip user's own audio stream to prevent feedback
if (userStreamId && stream.streamID === userStreamId) {
console.log('🚫 Skipping user\'s own stream:', stream.streamID)
continue
}
try {
console.log('🔗 Playing AI agent audio stream:', stream.streamID)
// Connect AI agent audio stream to playback
const mediaStream = await this.zg!.startPlayingStream(stream.streamID)
if (mediaStream) {
const remoteView = await this.zg!.createRemoteStreamView(mediaStream)
if (remoteView && this.audioElement) {
await remoteView.play(this.audioElement, {
enableAutoplayDialog: false,
muted: false
})
console.log('✅ AI agent audio connected and playing')
this.audioElement.muted = false
this.audioElement.volume = 0.8
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ Failed to play agent audio stream:', error)
}
}
} else if (updateType === 'DELETE') {
console.log('📴 AI agent audio stream disconnected')
if (this.audioElement) {
this.audioElement.srcObject = null
}
}
})
}4.3 Voice Session Coordination
Join voice rooms and establish bidirectional audio communication:
async joinRoom(roomId: string, userId: string): Promise<boolean> {
if (!this.zg) {
console.error('❌ ZEGO not initialized')
return false
}
try {
this.currentRoomId = roomId
this.currentUserId = userId
// Get authentication token for voice session
console.log('🔑 Getting token for user:', userId)
const { token } = await agentAPI.getToken(userId)
// Join ZEGOCLOUD room for voice communication
console.log('🚪 Logging into room:', roomId)
await this.zg.loginRoom(roomId, token, {
userID: userId,
userName: userId
})
// Enable voice message reception from AI agent
console.log('📢 Enabling voice message reception')
this.zg.callExperimentalAPI({
method: 'onRecvRoomChannelMessage',
params: {}
})
// Create local audio stream for voice input
console.log('🎤 Creating local audio stream')
const localStream = await this.zg.createZegoStream({
camera: {
video: false,
audio: true
}
})
if (localStream) {
this.localStream = localStream
const streamId = `${userId}_stream`
// Publish user audio stream to AI agent
console.log('📤 Publishing audio stream:', streamId)
await this.zg.startPublishingStream(streamId, localStream)
console.log('✅ Voice room joined successfully')
return true
} else {
throw new Error('Failed to create local audio stream')
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('❌ Failed to join voice room:', error)
return false
}
}The complete ZEGOCLOUD integration code is available here.
5. Voice Processing Hook
5.1 Voice Event Handling
Manage voice transcription and AI response streaming with real-time state updates:
const setupMessageHandlers = useCallback((conv: ConversationMemory) => {
const handleRoomMessage = (data: any) => {
try {
const { Cmd, Data: msgData } = data
console.log('Voice message received:', { Cmd, msgData })
if (Cmd === 3) {
// User voice transcription processing
const { Text: transcript, EndFlag, MessageId } = msgData
if (transcript && transcript.trim()) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT', payload: transcript })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'listening' })
if (EndFlag) {
// Complete voice input - create user message
const messageId = MessageId || `voice_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
const userMessage: Message = {
id: messageId,
content: transcript.trim(),
sender: 'user',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'voice',
transcript: transcript.trim()
}
addMessageSafely(userMessage, conv.id)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT', payload: '' })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'thinking' })
}
}
} else if (Cmd === 4) {
// AI agent voice response streaming
const { Text: content, MessageId, EndFlag } = msgData
if (!content || !MessageId) return
if (EndFlag) {
// Final response chunk - complete the message
const currentStreaming = streamingMessages.current.get(MessageId) || ''
const finalContent = currentStreaming + content
dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE_MESSAGE', payload: {
id: MessageId,
updates: {
content: finalContent,
isStreaming: false
}
}})
streamingMessages.current.delete(MessageId)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
// Save completed AI response
const finalMessage: Message = {
id: MessageId,
content: finalContent,
sender: 'ai',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text'
}
memoryService.addMessage(conv.id, finalMessage)
} else {
// Streaming response chunk - update in real-time
const currentStreaming = streamingMessages.current.get(MessageId) || ''
const updatedContent = currentStreaming + content
streamingMessages.current.set(MessageId, updatedContent)
if (!processedMessageIds.current.has(MessageId)) {
// Create new streaming message
const streamingMessage: Message = {
id: MessageId,
content: updatedContent,
sender: 'ai',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text',
isStreaming: true
}
processedMessageIds.current.add(MessageId)
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_MESSAGE', payload: streamingMessage })
} else {
// Update existing streaming message
dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE_MESSAGE', payload: {
id: MessageId,
updates: { content: updatedContent, isStreaming: true }
}})
}
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'speaking' })
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error handling voice message:', error)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
}
}
zegoService.current.onRoomMessage(handleRoomMessage)
}, [addMessageSafely])5.2 Voice Session Management
Coordinate voice session lifecycle with proper cleanup:
const startSession = useCallback(async (existingConversationId?: string): Promise<boolean> => {
if (state.isLoading || state.isConnected) return false
dispatch({ type: 'SET_LOADING', payload: true })
try {
const roomId = `room_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
const userId = `user_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
// Initialize ZEGO voice engine
console.log('Initializing ZEGO voice service...')
await zegoService.current.initialize()
// Join voice room for bidirectional audio
console.log('Joining voice room:', roomId)
const joinResult = await zegoService.current.joinRoom(roomId, userId)
if (!joinResult) throw new Error('Failed to join ZEGO voice room')
// Start AI agent for voice processing
console.log('Starting AI voice agent...')
const result = await agentAPI.startSession(roomId, userId)
const conv = initializeConversation(existingConversationId)
if (!conv) throw new Error('Failed to initialize conversation')
const newSession: ChatSession = {
roomId,
userId,
agentInstanceId: result.agentInstanceId,
isActive: true,
conversationId: conv.id,
voiceSettings: defaultVoiceSettings
}
dispatch({ type: 'SET_SESSION', payload: newSession })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_CONNECTED', payload: true })
setupMessageHandlers(conv)
console.log('Voice session started successfully')
return true
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to start voice session:', error)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_ERROR', payload: error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Failed to start voice session' })
return false
} finally {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_LOADING', payload: false })
}
}, [state.isLoading, state.isConnected, initializeConversation, setupMessageHandlers])6. Application Integration
The complete voice agent implementation is available in the Zego Agent GitHub repository. Run both servers to test voice functionality:
Start the backend:
cd server && npm run devStart the frontend:
cd client && npm run devThe voice agent processes speech through ZEGOCLOUD’s ASR, generates responses via Dashscope, and delivers audio through CosyVoice synthesis – all coordinated through real-time WebRTC streams.
Run a Demo
Conclusion
This AI voice agent makes conversations smooth and natural, without complicated setup. Users can simply speak and get real-time, intelligent responses.
With ZEGOCLOUD handling audio processing, streaming, and speech recognition, you can focus on creating engaging experiences instead of technical overhead.
Its flexible and scalable foundation lets you build AI voice agent that match your needs. You can customize personality, connect with business systems, and extend features while keeping a reliable core for voice interactions.
FAQ
Q1: How to create an AI voice agent?
You can create an AI voice agent by combining speech recognition, natural language processing, and text-to-speech. Using platforms like ZEGOCLOUD, you can simplify this process with one SDK that manages the full voice pipeline.
Q2: Can I create my own AI agent?
Yes. With modern APIs and SDKs, anyone can build a custom AI agent. You do not need to train models from scratch since you can integrate existing AI services to handle speech and conversation.
Q3: How do I build my own AI voice?
To build your own AI voice, you need text-to-speech technology that converts responses into natural speech. ZEGOCLOUD integrates this with speech recognition and AI processing so you can create a complete voice interaction system.
Q4: What is the architecture of a voice AI agent?
A voice AI agent typically has four layers: speech recognition to capture input, natural language processing to understand meaning, decision-making powered by a language model, and voice synthesis to respond naturally. ZEGOCLOUD connects these components through a unified architecture.
Let’s Build APP Together
Start building with real-time video, voice & chat SDK for apps today!










