Voice-first interfaces are transforming the way people interact with software. An AI voice assistant lets users speak naturally to get answers, complete tasks, and access information without touching a screen. By combining speech recognition, language models, and text-to-speech synthesis, you can create an AI-powered voice assistant that feels like talking to a real person.
This tutorial walks through building a fully functional AI voice assistant using ZEGOCLOUD. Users can speak or type, and the assistant responds with both text and natural-sounding speech. The system handles real-time audio streaming, maintains conversation context, and provides visual feedback throughout the interaction.
Building an AI-Powered Voice Assistant with ZEGOCLOUD
Voice assistants work by connecting several technologies: speech-to-text converts spoken words into text, a language model generates intelligent responses, and text-to-speech delivers those responses as audio. ZEGOCLOUD’s Conversational AI handles all three components through a unified API.
The system architecture places an AI agent inside a real-time communication room:
- The user connects to a ZEGOCLOUD room and streams microphone audio
- The AI agent receives the audio, transcribes it, generates a response, and speaks it back
- The web application displays the conversation and manages user interactions.
Prerequisites
Before building your AI voice assistant, you need:
- A ZEGOCLOUD account with AI Agent access → Sign up here
- Node.js 18+ installed on your machine
- Your AppID and ServerSecret from the ZEGOCLOUD console
- A DashScope API key (use
zego_testduring trial) - Chrome or Edge browser with microphone permissions
- Basic familiarity with React and Node.js
Step 1. Project Architecture and Setup
The complete source code is available at zego-assistant.
1.1 System Design
The AI-powered voice assistant splits into two parts:
Backend Server
- Authenticates with ZEGOCLOUD APIs using signed requests
- Registers the AI agent with voice and language settings
- Creates and destroys agent instances for each conversation
- Generates access tokens for frontend connections
Frontend Application
- Connects to ZEGOCLOUD rooms via WebRTC
- Captures and streams microphone audio
- Receives transcriptions and AI responses in real-time
- Stores conversation history locally
- Provides voice and text input options
Here’s the flow diagram:
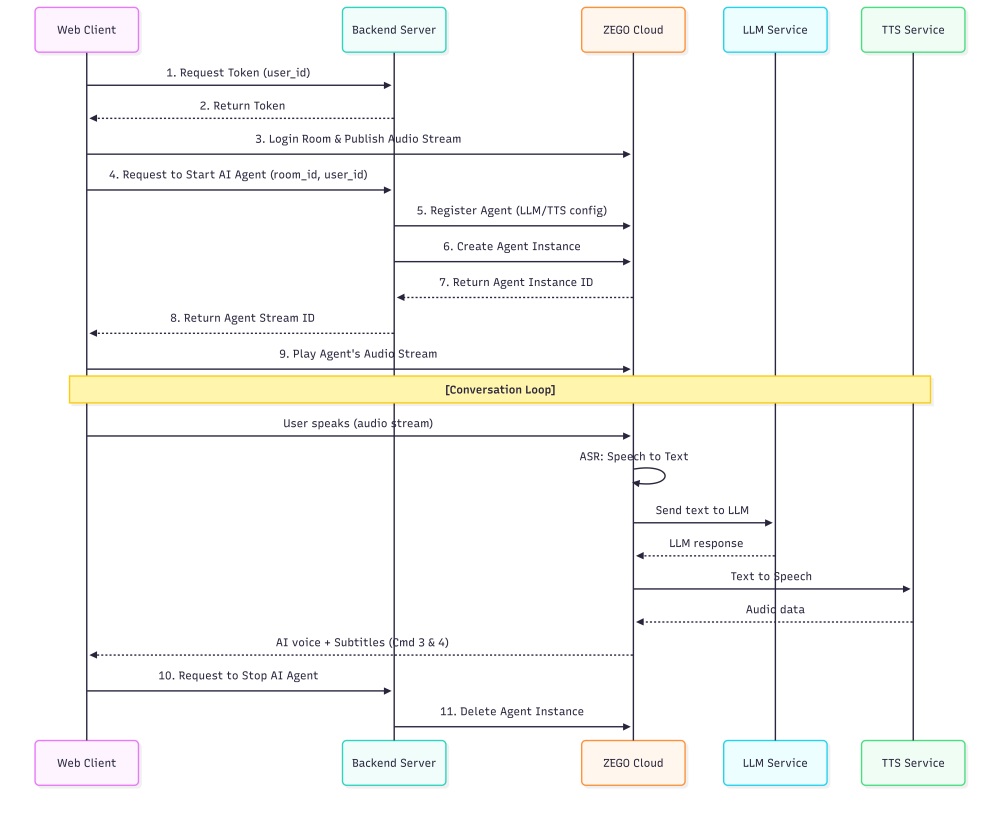
All audio processing happens on ZEGOCLOUD’s infrastructure. Your server handles authentication and configuration while the frontend manages the user experience.
1.2 Project Initialization
Set up the directory structure:
mkdir zego-assistant && cd zego-assistant
mkdir server clientServer Dependencies
cd server
npm init -y
npm install express cors dotenv axios typescript tsx
npm install --save-dev @types/express @types/cors @types/nodeCreate server/.env:
ZEGO_APP_ID=your_numeric_app_id
ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET=your_32_character_secret
DASHSCOPE_API_KEY=your_dashscope_api_key
PORT=8080Add scripts to server/package.json:
{
"scripts": {
"dev": "tsx watch src/server.ts",
"build": "tsc",
"start": "node dist/server.js"
}
}Client Dependencies
cd ../client
npm create vite@latest . -- --template react-ts
npm install zego-express-engine-webrtc axios framer-motion lucide-react tailwindcss zodCreate client/.env:
VITE_ZEGO_APP_ID=your_numeric_app_id
VITE_ZEGO_SERVER=wss://webrtc-api.zegocloud.com/ws
VITE_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8080Configuration Validation
Catch missing environment variables early:
// client/src/config.ts
import { z } from 'zod'
const configSchema = z.object({
ZEGO_APP_ID: z.string().min(1, 'ZEGO App ID is required'),
API_BASE_URL: z.string().url('Valid API base URL required'),
ZEGO_SERVER: z.string().url('Valid ZEGO server URL required'),
})
const rawConfig = {
ZEGO_APP_ID: import.meta.env.VITE_ZEGO_APP_ID,
API_BASE_URL: import.meta.env.VITE_API_BASE_URL,
ZEGO_SERVER: import.meta.env.VITE_ZEGO_SERVER || 'wss://webrtc-api.zegocloud.com/ws',
}
export const config = configSchema.parse(rawConfig)The app fails fast with clear error messages if the configuration is incomplete.
Step 2. Voice Assistant Backend
The server authenticates API requests, configures the AI agent, and manages conversation sessions.
2.1 API Authentication
ZEGOCLOUD requires MD5-signed requests:
// server/src/server.ts
import express from 'express'
import crypto from 'crypto'
import axios from 'axios'
import cors from 'cors'
import dotenv from 'dotenv'
import { createRequire } from 'module'
const require = createRequire(import.meta.url)
const { generateToken04 } = require('../zego-token.cjs')
dotenv.config()
const app = express()
app.use(express.json())
app.use(cors())
const CONFIG = {
ZEGO_APP_ID: process.env.ZEGO_APP_ID!,
ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET: process.env.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET!,
ZEGO_API_BASE_URL: 'https://aigc-aiagent-api.zegotech.cn/',
PORT: parseInt(process.env.PORT || '8080', 10)
}
function generateZegoSignature(action: string) {
const timestamp = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000)
const nonce = crypto.randomBytes(8).toString('hex')
const signString = CONFIG.ZEGO_APP_ID + nonce + CONFIG.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET + timestamp
const signature = crypto.createHash('md5').update(signString).digest('hex')
return {
Action: action,
AppId: CONFIG.ZEGO_APP_ID,
SignatureNonce: nonce,
SignatureVersion: '2.0',
Timestamp: timestamp,
Signature: signature
}
}
async function makeZegoRequest(action: string, body: object = {}) {
const queryParams = generateZegoSignature(action)
const queryString = Object.entries(queryParams)
.map(([k, v]) => `${k}=${encodeURIComponent(String(v))}`)
.join('&')
const url = `${CONFIG.ZEGO_API_BASE_URL}?${queryString}`
const response = await axios.post(url, body, {
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
timeout: 30000
})
return response.data
}Every API call includes a fresh signature with timestamp and nonce to prevent replay attacks.
2.2 Voice Agent Configuration
The agent definition controls how your ai voice assistant sounds and responds:
// server/src/server.ts
let REGISTERED_AGENT_ID: string | null = null
async function registerAgent(): Promise<string> {
if (REGISTERED_AGENT_ID) return REGISTERED_AGENT_ID
const agentId = `agent_${Date.now()}`
const agentConfig = {
AgentId: agentId,
Name: 'AI Assistant',
LLM: {
Url: 'https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1/chat/completions',
ApiKey: 'zego_test',
Model: 'qwen-plus',
SystemPrompt: `You are a helpful AI assistant. Provide clear, accurate, and useful information on a wide range of topics. Be concise but thorough in your responses. Keep responses conversational and under 100 words for natural voice flow. Help users with questions, tasks, and problem-solving in a friendly and professional manner.`,
Temperature: 0.7,
TopP: 0.9,
Params: { max_tokens: 200 }
},
TTS: {
Vendor: 'ByteDance',
Params: {
app: { appid: 'zego_test', token: 'zego_test', cluster: 'volcano_tts' },
speed_ratio: 1,
volume_ratio: 1,
pitch_ratio: 1,
audio: { rate: 24000 }
}
},
ASR: {
Vendor: 'Tencent',
Params: {
engine_model_type: '16k_en',
hotword_list: 'assistant|10,help|8,question|8,answer|8'
},
VADSilenceSegmentation: 1500,
PauseInterval: 2000
}
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('RegisterAgent', agentConfig)
if (result.Code !== 0) {
throw new Error(`RegisterAgent failed: ${result.Message}`)
}
REGISTERED_AGENT_ID = agentId
return agentId
}Voice-specific settings:
- VADSilenceSegmentation: 1500ms of silence triggers end-of-speech detection
- PauseInterval: 2000ms wait before finalizing transcription
- speed_ratio: Controls speech pace (1.0 = normal)
- max_tokens: 200 keeps responses brief for natural conversation flow
The agent registers once and serves all user sessions.
2.3 Session Endpoints
// server/src/server.ts
app.post('/api/start', async (req, res) => {
const { room_id, user_id, user_stream_id } = req.body
if (!room_id || !user_id) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'room_id and user_id required' })
return
}
const agentId = await registerAgent()
const userStreamId = user_stream_id || `${user_id}_stream`
const agentUserId = `agent_${room_id}`
const agentStreamId = `agent_stream_${room_id}`
const instanceConfig = {
AgentId: agentId,
UserId: user_id,
RTC: {
RoomId: room_id,
AgentUserId: agentUserId,
AgentStreamId: agentStreamId,
UserStreamId: userStreamId
},
MessageHistory: {
SyncMode: 1,
Messages: [],
WindowSize: 10
},
AdvancedConfig: {
InterruptMode: 0
}
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('CreateAgentInstance', instanceConfig)
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message })
return
}
res.json({
success: true,
agentInstanceId: result.Data?.AgentInstanceId,
agentUserId,
agentStreamId,
userStreamId
})
})
app.post('/api/send-message', async (req, res) => {
const { agent_instance_id, message } = req.body
if (!agent_instance_id || !message) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'agent_instance_id and message required' })
return
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('SendAgentInstanceLLM', {
AgentInstanceId: agent_instance_id,
Text: message,
AddQuestionToHistory: true,
AddAnswerToHistory: true
})
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message })
return
}
res.json({ success: true })
})
app.get('/api/token', (req, res) => {
const userId = req.query.user_id as string
if (!userId) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'user_id required' })
return
}
const payload = {
room_id: '',
privilege: { 1: 1, 2: 1 },
stream_id_list: null
}
const token = generateToken04(
parseInt(CONFIG.ZEGO_APP_ID, 10),
userId,
CONFIG.ZEGO_SERVER_SECRET,
3600,
JSON.stringify(payload)
)
res.json({ token })
})
app.post('/api/stop', async (req, res) => {
const { agent_instance_id } = req.body
if (!agent_instance_id) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'agent_instance_id required' })
return
}
const result = await makeZegoRequest('DeleteAgentInstance', {
AgentInstanceId: agent_instance_id
})
if (result.Code !== 0) {
res.status(400).json({ error: result.Message })
return
}
res.json({ success: true })
})
app.listen(CONFIG.PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${CONFIG.PORT}`)
})Each session gets a unique room, isolating conversations from each other.
Step 3. Real-Time Voice Communication
The frontend uses ZegoExpressEngine for WebRTC audio streaming and message handling.
3.1 ZEGO Service Implementation
// client/src/services/zego.ts
import { ZegoExpressEngine } from 'zego-express-engine-webrtc'
import { config } from '../config'
import { agentAPI } from './api'
export class ZegoService {
private static instance: ZegoService
private zg: ZegoExpressEngine | null = null
private isInitialized = false
private currentRoomId: string | null = null
private currentUserId: string | null = null
private localStream: any = null
private audioElement: HTMLAudioElement | null = null
static getInstance(): ZegoService {
if (!ZegoService.instance) {
ZegoService.instance = new ZegoService()
}
return ZegoService.instance
}
async initialize(): Promise<void> {
if (this.isInitialized) return
this.zg = new ZegoExpressEngine(
parseInt(config.ZEGO_APP_ID),
config.ZEGO_SERVER
)
this.setupEventListeners()
this.setupAudioElement()
this.isInitialized = true
}
private setupAudioElement(): void {
this.audioElement = document.getElementById('ai-audio-output') as HTMLAudioElement
if (!this.audioElement) {
this.audioElement = document.createElement('audio')
this.audioElement.id = 'ai-audio-output'
this.audioElement.autoplay = true
this.audioElement.style.display = 'none'
document.body.appendChild(this.audioElement)
}
this.audioElement.volume = 0.8
}
}The singleton pattern ensures one engine instance per browser tab.
3.2 Voice Stream Handling
// client/src/services/zego.ts (continued)
private setupEventListeners(): void {
if (!this.zg) return
this.zg.on('recvExperimentalAPI', (result: any) => {
const { method, content } = result
if (method === 'onRecvRoomChannelMessage') {
try {
const message = JSON.parse(content.msgContent)
this.handleRoomMessage(message)
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to parse room message:', error)
}
}
})
this.zg.on('roomStreamUpdate', async (_roomID, updateType, streamList) => {
if (updateType === 'ADD') {
for (const stream of streamList) {
const userStreamId = this.currentUserId ? `${this.currentUserId}_stream` : null
if (userStreamId && stream.streamID === userStreamId) {
continue
}
try {
const mediaStream = await this.zg!.startPlayingStream(stream.streamID)
if (mediaStream) {
const remoteView = await this.zg!.createRemoteStreamView(mediaStream)
if (remoteView && this.audioElement) {
await remoteView.play(this.audioElement, {
enableAutoplayDialog: false,
muted: false
})
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to play agent stream:', error)
}
}
}
})
}
private messageCallback: ((message: any) => void) | null = null
private handleRoomMessage(message: any): void {
if (this.messageCallback) {
this.messageCallback(message)
}
}
onRoomMessage(callback: (message: any) => void): void {
this.messageCallback = callback
}The roomStreamUpdate event fires when the AI agent starts speaking, connecting its audio output to the user’s speakers.
3.3 Room and Microphone Control
// client/src/services/zego.ts (continued)
async joinRoom(roomId: string, userId: string): Promise<boolean> {
if (!this.zg) return false
if (this.currentRoomId === roomId && this.currentUserId === userId) {
return true
}
try {
if (this.currentRoomId) {
await this.leaveRoom()
}
this.currentRoomId = roomId
this.currentUserId = userId
const { token } = await agentAPI.getToken(userId)
await this.zg.loginRoom(roomId, token, {
userID: userId,
userName: userId
})
this.zg.callExperimentalAPI({
method: 'onRecvRoomChannelMessage',
params: {}
})
const localStream = await this.zg.createZegoStream({
camera: { video: false, audio: true }
})
if (localStream) {
this.localStream = localStream
const streamId = `${userId}_stream`
await this.zg.startPublishingStream(streamId, localStream)
return true
}
throw new Error('Failed to create local stream')
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to join room:', error)
this.currentRoomId = null
this.currentUserId = null
return false
}
}
async enableMicrophone(enabled: boolean): Promise<boolean> {
if (!this.localStream) return false
const audioTrack = this.localStream.getAudioTracks()[0]
if (audioTrack) {
audioTrack.enabled = enabled
return true
}
return false
}
async leaveRoom(): Promise<void> {
if (!this.zg || !this.currentRoomId) return
if (this.currentUserId && this.localStream) {
await this.zg.stopPublishingStream(`${this.currentUserId}_stream`)
}
if (this.localStream) {
this.zg.destroyStream(this.localStream)
this.localStream = null
}
await this.zg.logoutRoom()
this.currentRoomId = null
this.currentUserId = null
}The enableMicrophone function toggles voice transmission without disconnecting from the room.
Step 4. Conversation State Management
The useChat hook coordinates voice input, message display, and session lifecycle.
4.1 State and Reducer
// client/src/hooks/useChat.ts
import { useCallback, useRef, useReducer } from 'react'
import { ZegoService } from '../services/zego'
import { agentAPI } from '../services/api'
import { memoryService } from '../services/memory'
interface ChatState {
messages: Message[]
session: ChatSession | null
isLoading: boolean
isConnected: boolean
isRecording: boolean
currentTranscript: string
agentStatus: 'idle' | 'listening' | 'thinking' | 'speaking'
error: string | null
}
type ChatAction =
| { type: 'ADD_MESSAGE'; payload: Message }
| { type: 'SET_SESSION'; payload: ChatSession | null }
| { type: 'SET_CONNECTED'; payload: boolean }
| { type: 'SET_RECORDING'; payload: boolean }
| { type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT'; payload: string }
| { type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS'; payload: 'idle' | 'listening' | 'thinking' | 'speaking' }
| { type: 'SET_LOADING'; payload: boolean }
| { type: 'SET_ERROR'; payload: string | null }
function chatReducer(state: ChatState, action: ChatAction): ChatState {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD_MESSAGE':
return { ...state, messages: [...state.messages, action.payload] }
case 'SET_SESSION':
return { ...state, session: action.payload }
case 'SET_CONNECTED':
return { ...state, isConnected: action.payload }
case 'SET_RECORDING':
return { ...state, isRecording: action.payload }
case 'SET_TRANSCRIPT':
return { ...state, currentTranscript: action.payload }
case 'SET_AGENT_STATUS':
return { ...state, agentStatus: action.payload }
case 'SET_LOADING':
return { ...state, isLoading: action.payload }
case 'SET_ERROR':
return { ...state, error: action.payload }
default:
return state
}
}
export const useChat = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(chatReducer, {
messages: [],
session: null,
isLoading: false,
isConnected: false,
isRecording: false,
currentTranscript: '',
agentStatus: 'idle',
error: null
})
const zegoService = useRef(ZegoService.getInstance())
const processedMessageIds = useRef(new Set<string>())
}The agentStatus field drives UI feedback: users see when the assistant is listening, thinking, or speaking.
4.2 Voice Event Processing
// client/src/hooks/useChat.ts (continued)
const setupMessageHandlers = useCallback((conversationId: string) => {
const handleRoomMessage = (data: any) => {
const { Cmd, Data: msgData } = data
// Cmd 3: Speech-to-text results
if (Cmd === 3) {
const { Text: transcript, EndFlag, MessageId } = msgData
if (transcript && transcript.trim()) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT', payload: transcript })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'listening' })
if (EndFlag) {
const userMessage: Message = {
id: MessageId || `voice_${Date.now()}`,
content: transcript.trim(),
sender: 'user',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'voice'
}
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_MESSAGE', payload: userMessage })
memoryService.addMessage(conversationId, userMessage)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_TRANSCRIPT', payload: '' })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'thinking' })
}
}
}
// Cmd 4: AI response
if (Cmd === 4) {
const { Text: content, MessageId, EndFlag } = msgData
if (!content || !MessageId) return
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'speaking' })
if (EndFlag) {
const aiMessage: Message = {
id: MessageId,
content,
sender: 'ai',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text'
}
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_MESSAGE', payload: aiMessage })
memoryService.addMessage(conversationId, aiMessage)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
}
}
}
zegoService.current.onRoomMessage(handleRoomMessage)
}, [])Real-time transcription shows users their words as they speak, with EndFlag marking when speech recognition completes.
4.3 Session and Input Controls
// client/src/hooks/useChat.ts (continued)
const startSession = useCallback(async (): Promise<boolean> => {
if (state.isLoading || state.isConnected) return false
dispatch({ type: 'SET_LOADING', payload: true })
try {
const roomId = `room_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
const userId = `user_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 6)}`
await zegoService.current.initialize()
const joinResult = await zegoService.current.joinRoom(roomId, userId)
if (!joinResult) throw new Error('Failed to join ZEGO room')
const result = await agentAPI.startSession(roomId, userId)
const conversation = memoryService.createOrGetConversation()
const newSession: ChatSession = {
roomId,
userId,
agentInstanceId: result.agentInstanceId,
isActive: true,
conversationId: conversation.id
}
dispatch({ type: 'SET_SESSION', payload: newSession })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_CONNECTED', payload: true })
setupMessageHandlers(conversation.id)
return true
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_ERROR', payload: error.message })
return false
} finally {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_LOADING', payload: false })
}
}, [state.isLoading, state.isConnected, setupMessageHandlers])
const sendTextMessage = useCallback(async (content: string) => {
if (!state.session?.agentInstanceId || !state.conversation) return
const trimmedContent = content.trim()
if (!trimmedContent) return
try {
const userMessage: Message = {
id: `text_${Date.now()}`,
content: trimmedContent,
sender: 'user',
timestamp: Date.now(),
type: 'text'
}
dispatch({ type: 'ADD_MESSAGE', payload: userMessage })
memoryService.addMessage(state.conversation.id, userMessage)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'thinking' })
await agentAPI.sendMessage(state.session.agentInstanceId, trimmedContent)
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_ERROR', payload: 'Failed to send message' })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
}
}, [state.session, state.conversation])
const toggleVoiceRecording = useCallback(async () => {
if (!state.isConnected) return
try {
if (state.isRecording) {
await zegoService.current.enableMicrophone(false)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_RECORDING', payload: false })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
} else {
const success = await zegoService.current.enableMicrophone(true)
if (success) {
dispatch({ type: 'SET_RECORDING', payload: true })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'listening' })
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to toggle recording:', error)
}
}, [state.isConnected, state.isRecording])
const endSession = useCallback(async () => {
if (!state.session) return
try {
if (state.isRecording) {
await zegoService.current.enableMicrophone(false)
dispatch({ type: 'SET_RECORDING', payload: false })
}
if (state.session.agentInstanceId) {
await agentAPI.stopSession(state.session.agentInstanceId)
}
await zegoService.current.leaveRoom()
dispatch({ type: 'SET_SESSION', payload: null })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_CONNECTED', payload: false })
dispatch({ type: 'SET_AGENT_STATUS', payload: 'idle' })
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to end session:', error)
}
}, [state.session, state.isRecording])
return {
...state,
startSession,
sendTextMessage,
toggleVoiceRecording,
endSession
}Users can speak or type—both inputs flow through the same AI processing pipeline.
4.4 Conversation Memory
Store conversations in localStorage for persistence:
// client/src/services/memory.ts
import type { ConversationMemory, Message } from '../types'
class MemoryService {
private conversations: Map<string, ConversationMemory> = new Map()
constructor() {
this.loadFromStorage()
}
private loadFromStorage(): void {
const stored = localStorage.getItem('ai_conversations')
if (stored) {
const conversations: ConversationMemory[] = JSON.parse(stored)
conversations.forEach(conv => {
this.conversations.set(conv.id, conv)
})
}
}
private saveToStorage(): void {
const conversations = Array.from(this.conversations.values())
localStorage.setItem('ai_conversations', JSON.stringify(conversations))
}
createOrGetConversation(id?: string): ConversationMemory {
const conversationId = id || `conv_${Date.now()}_${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9)}`
if (this.conversations.has(conversationId)) {
return this.conversations.get(conversationId)!
}
const newConversation: ConversationMemory = {
id: conversationId,
title: 'New Conversation',
messages: [],
createdAt: Date.now(),
updatedAt: Date.now()
}
this.conversations.set(conversationId, newConversation)
this.saveToStorage()
return newConversation
}
addMessage(conversationId: string, message: Message): void {
const conversation = this.conversations.get(conversationId)
if (!conversation) return
conversation.messages.push(message)
conversation.updatedAt = Date.now()
if (conversation.messages.length === 1 && message.sender === 'user') {
conversation.title = message.content.slice(0, 50)
}
this.saveToStorage()
}
getAllConversations(): ConversationMemory[] {
return Array.from(this.conversations.values())
.sort((a, b) => b.updatedAt - a.updatedAt)
}
deleteConversation(conversationId: string): void {
this.conversations.delete(conversationId)
this.saveToStorage()
}
}
export const memoryService = new MemoryService()Users can close the browser and return to find their conversation history intact.
Step 5. Voice Interface Components
The UI provides clear feedback during voice interactions.
5.1 Main Chat Component
// client/src/components/ChatSession.tsx
import { useEffect, useRef } from 'react'
import { motion } from 'framer-motion'
import { MessageBubble } from './Chat/MessageBubble'
import { VoiceInput } from './VoiceInput'
import { useChat } from '../hooks/useChat'
import { MessageCircle, Phone, PhoneOff } from 'lucide-react'
export const ChatSession = () => {
const messagesEndRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null)
const {
messages,
isLoading,
isConnected,
isRecording,
currentTranscript,
agentStatus,
startSession,
sendTextMessage,
toggleVoiceRecording,
endSession
} = useChat()
useEffect(() => {
messagesEndRef.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth' })
}, [messages])
if (!isConnected && messages.length === 0) {
return (
<div className="flex flex-col h-full bg-black">
<audio id="ai-audio-output" autoPlay style={{ display: 'none' }} />
<div className="flex-1 flex flex-col items-center justify-center">
<motion.div initial={{ opacity: 0, y: 20 }} animate={{ opacity: 1, y: 0 }}>
<div className="w-24 h-24 bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-600 to-blue-700 rounded-full flex items-center justify-center mb-8 mx-auto">
<MessageCircle className="w-12 h-12 text-white" />
</div>
<h2 className="text-3xl font-semibold mb-4 text-center">AI Voice Assistant</h2>
<p className="text-gray-400 mb-10 max-w-md text-center">
Speak naturally or type your questions. I'll respond with voice and text.
</p>
<button
onClick={startSession}
disabled={isLoading}
className="px-8 py-4 bg-blue-600 hover:bg-blue-700 rounded-full flex items-center space-x-3 mx-auto"
>
<Phone className="w-5 h-5" />
<span>{isLoading ? 'Connecting...' : 'Start Conversation'}</span>
</button>
</motion.div>
</div>
</div>
)
}
return (
<div className="flex flex-col h-full bg-black">
<audio id="ai-audio-output" autoPlay style={{ display: 'none' }} />
{/* Voice Status Indicator */}
<div className="bg-gray-900/50 border-b border-gray-800 px-6 py-3">
<div className="flex items-center justify-between">
<div className="flex items-center space-x-3">
<div className={`w-3 h-3 rounded-full ${isConnected ? 'bg-green-400 animate-pulse' : 'bg-gray-600'}`} />
<span className="text-sm text-gray-400">
{agentStatus === 'listening' && '🎤 Listening...'}
{agentStatus === 'thinking' && '🧠 Processing...'}
{agentStatus === 'speaking' && '🔊 Speaking...'}
{agentStatus === 'idle' && 'Ready'}
</span>
</div>
{isConnected && (
<button
onClick={endSession}
className="px-4 py-2 bg-red-600/80 hover:bg-red-600 rounded-lg flex items-center space-x-2"
>
<PhoneOff className="w-4 h-4" />
<span>End</span>
</button>
)}
</div>
</div>
{/* Conversation */}
<div className="flex-1 overflow-y-auto px-6 py-6">
{messages.map((message) => (
<MessageBubble key={message.id} message={message} />
))}
{agentStatus === 'thinking' && (
<motion.div
initial={{ opacity: 0, y: 20 }}
animate={{ opacity: 1, y: 0 }}
className="flex justify-start mb-6"
>
<div className="flex items-center space-x-3">
<div className="w-10 h-10 bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-600 to-blue-700 rounded-full flex items-center justify-center">
<MessageCircle className="w-5 h-5 text-white" />
</div>
<div className="bg-gray-800 rounded-2xl px-5 py-3">
<div className="flex space-x-1">
<div className="w-2 h-2 bg-blue-400 rounded-full animate-bounce" />
<div className="w-2 h-2 bg-blue-400 rounded-full animate-bounce" style={{ animationDelay: '0.1s' }} />
<div className="w-2 h-2 bg-blue-400 rounded-full animate-bounce" style={{ animationDelay: '0.2s' }} />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</motion.div>
)}
<div ref={messagesEndRef} />
</div>
{/* Voice/Text Input */}
{isConnected && (
<VoiceInput
onSendMessage={sendTextMessage}
isRecording={isRecording}
onToggleRecording={toggleVoiceRecording}
currentTranscript={currentTranscript}
agentStatus={agentStatus}
/>
)}
</div>
)
}The status indicator shows exactly what the ai voice assistant is doing at each moment.
5.2 Voice Input Controls
// client/src/components/VoiceInput.tsx
import { useState } from 'react'
import { motion } from 'framer-motion'
import { Mic, MicOff, Send, Type } from 'lucide-react'
interface VoiceInputProps {
onSendMessage: (message: string) => void
isRecording: boolean
onToggleRecording: () => void
currentTranscript: string
agentStatus: 'idle' | 'listening' | 'thinking' | 'speaking'
}
export const VoiceInput = ({
onSendMessage,
isRecording,
onToggleRecording,
currentTranscript,
agentStatus
}: VoiceInputProps) => {
const [textInput, setTextInput] = useState('')
const [inputMode, setInputMode] = useState<'voice' | 'text'>('voice')
const handleSendText = () => {
if (textInput.trim()) {
onSendMessage(textInput.trim())
setTextInput('')
}
}
const handleKeyPress = (e: React.KeyboardEvent) => {
if (e.key === 'Enter' && !e.shiftKey) {
e.preventDefault()
handleSendText()
}
}
const isDisabled = agentStatus === 'thinking' || agentStatus === 'speaking'
return (
<div className="bg-gray-900 border-t border-gray-800 p-4">
<div className="max-w-4xl mx-auto">
{/* Input Mode Toggle */}
<div className="flex justify-center mb-4">
<div className="bg-gray-800 rounded-lg p-1 flex">
<button
onClick={() => setInputMode('voice')}
className={`px-4 py-2 rounded-md flex items-center space-x-2 ${
inputMode === 'voice' ? 'bg-blue-600 text-white' : 'text-gray-400'
}`}
>
<Mic className="w-4 h-4" />
<span>Voice</span>
</button>
<button
onClick={() => setInputMode('text')}
className={`px-4 py-2 rounded-md flex items-center space-x-2 ${
inputMode === 'text' ? 'bg-blue-600 text-white' : 'text-gray-400'
}`}
>
<Type className="w-4 h-4" />
<span>Text</span>
</button>
</div>
</div>
{inputMode === 'voice' ? (
<div className="flex flex-col items-center space-y-4">
{/* Live Transcription Display */}
{currentTranscript && (
<motion.div
initial={{ opacity: 0, y: 10 }}
animate={{ opacity: 1, y: 0 }}
className="bg-gray-800 rounded-lg p-4 max-w-2xl w-full"
>
<p className="text-gray-300 text-center">{currentTranscript}</p>
</motion.div>
)}
{/* Microphone Button */}
<motion.button
onClick={onToggleRecording}
disabled={isDisabled}
className={`w-16 h-16 rounded-full flex items-center justify-center ${
isRecording ? 'bg-red-600 hover:bg-red-700' : 'bg-blue-600 hover:bg-blue-700'
} ${isDisabled ? 'opacity-50 cursor-not-allowed' : ''}`}
whileTap={{ scale: 0.95 }}
>
{isRecording ? <MicOff className="w-6 h-6 text-white" /> : <Mic className="w-6 h-6 text-white" />}
</motion.button>
<p className="text-sm text-gray-400">
{isRecording ? 'Tap to stop' : 'Tap to speak'}
</p>
</div>
) : (
<div className="flex items-end space-x-3">
<textarea
value={textInput}
onChange={(e) => setTextInput(e.target.value)}
onKeyPress={handleKeyPress}
placeholder="Type your message..."
disabled={isDisabled}
className="flex-1 bg-gray-800 border border-gray-700 rounded-lg px-4 py-3 text-white resize-none focus:outline-none focus:border-blue-500"
rows={1}
/>
<button
onClick={handleSendText}
disabled={!textInput.trim() || isDisabled}
className="w-12 h-12 bg-blue-600 hover:bg-blue-700 disabled:opacity-50 rounded-lg flex items-center justify-center"
>
<Send className="w-5 h-5 text-white" />
</button>
</div>
)}
</div>
</div>
)
}The live transcription preview shows users their words as they speak, building confidence that the system is hearing them correctly.
5.3 Message Display
// client/src/components/Chat/MessageBubble.tsx
import { motion } from 'framer-motion'
import { User, Bot, Mic } from 'lucide-react'
export const MessageBubble = ({ message }) => {
const isUser = message.sender === 'user'
return (
<motion.div
initial={{ opacity: 0, y: 20 }}
animate={{ opacity: 1, y: 0 }}
className={`flex mb-6 ${isUser ? 'justify-end' : 'justify-start'}`}
>
<div className={`flex items-start space-x-3 max-w-2xl ${isUser ? 'flex-row-reverse space-x-reverse' : ''}`}>
<div className={`w-10 h-10 rounded-full flex items-center justify-center ${
isUser ? 'bg-gradient-to-br from-green-600 to-green-700' : 'bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-600 to-blue-700'
}`}>
{isUser ? <User className="w-5 h-5 text-white" /> : <Bot className="w-5 h-5 text-white" />}
</div>
<div className={`rounded-2xl px-5 py-3 ${
isUser ? 'bg-green-600 text-white' : 'bg-gray-800 text-gray-100'
}`}>
<p className="text-sm leading-relaxed whitespace-pre-wrap">{message.content}</p>
{message.type === 'voice' && (
<div className="flex items-center mt-2 text-xs opacity-70">
<Mic className="w-3 h-3 mr-1" />
<span>Voice input</span>
</div>
)}
</div>
</div>
</motion.div>
)
}Voice messages display with a microphone indicator so users can distinguish spoken from typed input.
Step 6. API Client
// client/src/services/api.ts
import axios from 'axios'
import { config } from '../config'
const api = axios.create({
baseURL: config.API_BASE_URL,
timeout: 30000,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
})
export const agentAPI = {
async startSession(roomId: string, userId: string) {
const response = await api.post('/api/start', {
room_id: roomId,
user_id: userId,
user_stream_id: `${userId}_stream`,
})
if (!response.data?.success) {
throw new Error(response.data?.error || 'Session start failed')
}
return {
agentInstanceId: response.data.agentInstanceId
}
},
async sendMessage(agentInstanceId: string, message: string) {
const response = await api.post('/api/send-message', {
agent_instance_id: agentInstanceId,
message: message.trim(),
})
if (!response.data?.success) {
throw new Error(response.data?.error || 'Message send failed')
}
},
async stopSession(agentInstanceId: string) {
await api.post('/api/stop', {
agent_instance_id: agentInstanceId,
})
},
async getToken(userId: string) {
const response = await api.get(`/api/token?user_id=${encodeURIComponent(userId)}`)
if (!response.data?.token) {
throw new Error('No token returned')
}
return { token: response.data.token }
}
}Step 7. Testing Your Voice Assistant
7.1 Start the Backend
cd server
npm install
npm run devVerify at http://localhost:8080/health:
{
"status": "healthy",
"timestamp": "2025-12-22T10:00:00.000Z",
"registered": false
}7.2 Start the Frontend
cd client
npm install
npm run devOpen http://localhost:5173 in Chrome or Edge.
Run a Demo
Conclusion
You now have a working AI-powered voice assistant that understands speech, generates intelligent responses, and speaks naturally. The system handles the complexity of real-time audio streaming, speech recognition, and voice synthesis through ZEGOCLOUD’s infrastructure.
From here, you can add wake word detection, multi-language support, or connect to external APIs for weather, calendar, or smart home control. The voice-first pattern works well for hands-free applications, accessibility features, or any situation where speaking is easier than typing.
FAQ
Q1. How do I build my own AI voice assistant?
Start by combining speech recognition, natural language processing, and text-to-speech. Use a conversational AI platform to handle real-time voice interaction, then integrate it into your app.
Q2. How do I create my own voice AI?
You create a voice AI by connecting speech-to-text, an AI model to understand user intent, and text-to-speech for replies. Using ready-made APIs can significantly speed up development.
Q3. How to build an AI voice agent?
Define the agent’s use case, design conversation flows, and connect real-time voice, AI processing, and responses. Test continuously to improve accuracy and user experience.
Q4. How to make your own AI to talk to?
Build a talking AI by enabling real-time audio input, AI-driven responses, and natural-sounding voice output. Start with simple conversations and expand capabilities over time.
Let’s Build APP Together
Start building with real-time video, voice & chat SDK for apps today!










