In today’s video-first world, real-time video quality has become one of the most decisive factors behind user engagement, retention, and product competitiveness. From live streaming and video conferencing to online education and social interaction, users no longer tolerate unstable, blurry, or visually inconsistent video experiences.
Against this backdrop, ZEGOCLOUD has built a comprehensive portfolio of advanced video algorithms designed specifically to elevate real-time video quality across devices, networks, and environments. These algorithms do far more than fix common visual issues — they establish a new benchmark for what modern video experiences should look like.
Below, we explore the core capabilities of ZEGOCLOUD’s video enhancement technologies and how we translate into measurable business value.
Why Real-Time Video Quality Matters
Global video traffic continues to surge, driven by live commerce, social video, cloud gaming, telehealth, and remote work. Public industry research consistently shows that poor video quality is among the top reasons for user churn in real-time applications. As networks become more heterogeneous and user devices more diverse, delivering consistently high real-time video quality is now a strategic necessity rather than a technical luxury.
ZEGOCLOUD’s video algorithms are engineered for this reality: high visual impact, low computational cost, and real-time performance at scale.
The Remarkable Capabilities of ZEGOCLOUD’s Video Algorithms
Low-Light Enhancement — Illuminating the Darkness
Low-light enhancement lies at the heart of ZEGOCLOUD’s mission to improve video clarity in challenging lighting conditions. In dim environments, video content often suffers from darkness, blur, and excessive noise, making details difficult to distinguish and degrading user experience.

Causes of Low-Light Images
- Insufficient or Absent Light Sources: This is a primary culprit, leaving the scene inadequately illuminated. Without proper lighting, the camera struggles to capture clear and detailed images, resulting in a dark and murky output.
- Uneven Illumination due to Backlighting or Shadows: Backlighting and shadows can create pockets of varying brightness within the frame. This uneven distribution of light makes it challenging to discern details, especially in areas with sharp contrast between light and dark regions.
- Incorrect Camera Configuration or Sensor Limitations: Sometimes, the camera settings might not be optimized for the given lighting conditions. Additionally, the inherent limitations of the camera’s sensor in capturing light and color accurately can contribute to low – quality images. For instance, certain sensors may have a narrow dynamic range, causing them to lose details in both bright and dark areas.
ZEGOCLOUD’s low-light enhancement algorithm demonstrates exceptional adaptability. It intelligently blends original and enhanced frames based on ambient brightness using a carefully designed piece-wise function that determines the optimal enhancement weight. This ensures balanced output — no over-exposure in bright areas and no under-enhancement in dark regions.
Extensive engineering optimizations significantly reduce computational complexity while preserving visual performance. As a result, the algorithm runs smoothly even on low-end devices, enabling consistently high real-time video quality regardless of hardware capability.
Video Denoising — Purifying Visual Disturbances
Video denoising removes unwanted visual artifacts that compromise viewing comfort and clarity. Noise can originate from camera sensors, environmental interference, compression, or transmission issues, producing grainy, distorted images.
Sources of Noise
- Sensor Noise: The sensor in your camera is like a sensitive detector, but it’s not without its quirks. Electrical signals within the sensor can generate noise, especially in low – light conditions or when the sensor is pushed to its limits. This noise can manifest as random speckles or graininess in the video.
- Environmental Noise: External factors such as ambient light fluctuations, electromagnetic interference from nearby devices, or even the temperature can introduce noise into the video. For example, if you’re shooting near a high – voltage power line, the electromagnetic radiation can disrupt the sensor’s signal, leading to visible noise in the footage.
- Compression Noise: When videos are compressed to reduce file size for easier storage or transmission, compression algorithms can sometimes introduce artifacts. Block – like patterns, known as block artifacts, and other forms of distortion can occur, especially when the compression ratio is high. This compression noise can significantly degrade the video quality, making it look pixelated or blurry.
- Transmission Noise: In the digital age, videos are often transmitted over networks. Network jitter, packet loss, or bandwidth limitations can cause noise to appear in the video during playback. This transmission – related noise can range from minor glitches to more severe disruptions, affecting the overall viewing experience.
Types of Noise
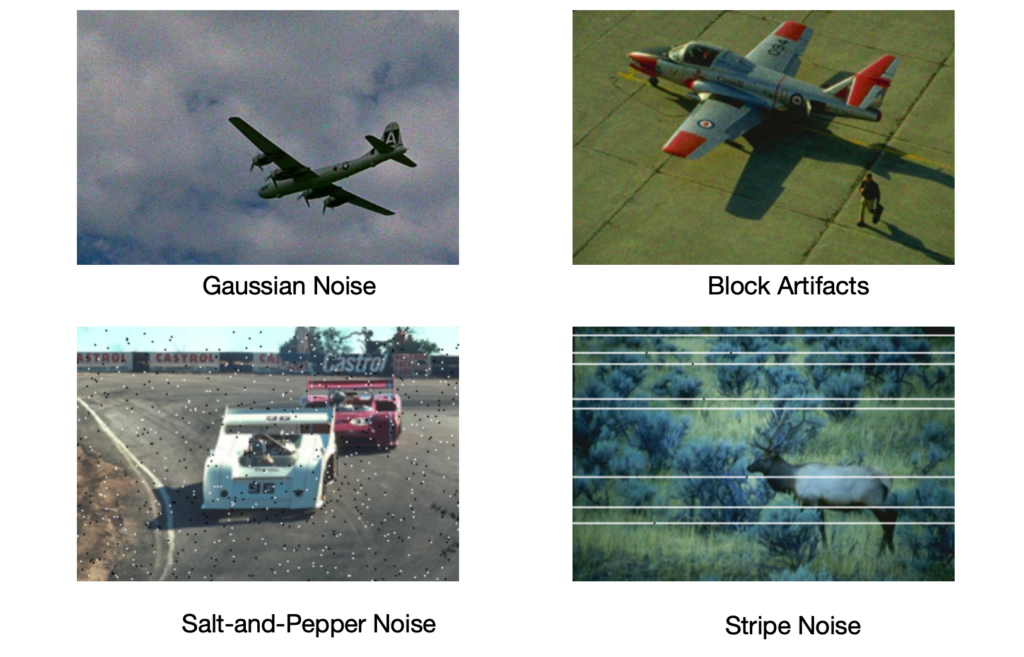
- Gaussian Noise: Named after the Gaussian distribution, this is one of the most common types of noise. It appears as a random variation in pixel values, giving the image or video a grainy appearance. Gaussian noise is often caused by sensor electronics and thermal noise.
- Speckle Noise: Commonly found in medical imaging (such as ultrasound and synthetic aperture radar images) and some types of microscopy, speckle noise looks like a granular pattern. It’s typically a result of the interference of scattered waves.
- Block Artifacts: These are the tell-tale signs of over-compression. Block artifacts appear as distinct rectangular blocks in the video, where the compression algorithm has grouped pixels together, sacrificing some detail for the sake of reducing file size.
- Salt-and-Pepper Noise: This type of noise appears as randomly distributed white (“salt”) and black (“pepper”) pixels across an image. With proper image processing techniques, it can be effectively identified and suppressed, helping restore visual clarity even when sensor inconsistencies, data transmission, or acquisition conditions introduce disruptions.
- Stripe Noise: Appearing as horizontal or vertical lines in the video, stripe noise can be due to issues with the camera’s sensor read-out process, interference, or problems with the image-processing pipeline.
ZEGOCLOUD’s denoising algorithm uses advanced signal-processing techniques to accurately identify and remove noise while preserving fine visual details. The result is clean, sharp output optimized for both viewing pleasure and analytical accuracy.
Color Enhancement — Unleashing Vivid Visuals
Color enhancement is the secret sauce that takes your images and videos from drab to dazzling. By adjusting the chroma and saturation, we can breathe new life into the visuals, making them more engaging and visually appealing. With the wide variety of device cameras out there, many struggle with producing vibrant colors. Issues like low saturation, a washed-out appearance, and dull colors are all too common during video capture. ZEGOCLOUD’s color enhancement feature steps in to solve these problems, intelligently boosting the saturation, dynamically adjusting the contrast and brightness, and transforming the overall look of the image or video.

Dual Goals of Color Enhancement
ZEGOCLOUD’s color enhancement technology is built around two equally important objectives: accuracy and visual appeal.
1. Color Restoration — Faithful to Reality
The primary goal is to reproduce colors as they appear in the real world.
Our algorithm minimizes color deviation so that what users see on screen remains as close as possible to the original scene.
This level of precision is especially critical in scenarios where color accuracy directly impacts results, including:
- Product photography and e-commerce
- Medical imaging and diagnostics
- Virtual reality and immersive environments
2. Aesthetic Appeal — Designed to Engage
Beyond accuracy, our system enhances colors in a refined, natural way to make visuals more immersive and emotionally engaging.
This produces richer, more attractive images that elevate experiences across:
- Marketing and promotional videos
- Social media content
- Creative and artistic productions
The result is not just correct color — but compelling visual storytelling.
Five Key Objectives of ZEGOCLOUD’s Color Enhancement Algorithm
1. Adaptability
The algorithm dynamically adjusts enhancement intensity based on the characteristics of each image. It recognizes areas that are already vivid and avoids over-saturating them, preserving natural balance. For example, in landscape scenes with bright flowers, the algorithm enhances color vibrancy while preserving natural appearance and visual authenticity.
2. Flaw-Free Adjustment
Common issues in color enhancement — such as over-saturation, detail loss, color deviation, and color banding — are carefully avoided.
Our algorithm fine-tunes every adjustment to ensure:
- Visual integrity is preserved
- Dark areas remain clean and smooth
- Color noise is not amplified
The final output remains stable, natural, and visually consistent.
3. Subjective Quality Improvement
Ultimately, color enhancement success is judged by human perception.
Through extensive testing with developers, evaluators, and end-users, we refined the algorithm to improve how images feel — not just how they measure. The focus is on producing visuals that the human eye naturally finds more pleasing and engaging.
4. Skin-Tone Protection
Maintaining realistic human skin tones is one of the most difficult challenges in color enhancement.
To solve this, we integrate a dedicated skin-tone protection mechanism. Using precise color thresholds in the YCbCr color space, the algorithm detects skin regions and preserves their natural appearance during enhancement — preventing unnatural orange hues or over-saturation.
This ensures people in videos and images always look lifelike.
5. System-Wide Compatibility
Color enhancement is designed to work seamlessly within a complete video processing pipeline.
It integrates smoothly with:
- Denoising
- Sharpening
- Compression
Whether in advanced post-production workflows or real-time video streaming systems, the algorithm enhances overall quality without interfering with other processing modules — delivering consistently superior visual performance.
To achieve these objectives, ZEGOCLOUD combines proven color-model-based techniques with proprietary natural-saturation adjustment algorithms, forming a balanced and highly reliable enhancement framework.
We leverage both the HSV and Lab color models, each contributing distinct strengths:
- HSV-based enhancement allows saturation to be adjusted independently from brightness and hue. This provides a direct and efficient way to increase color vividness without unintentionally affecting overall exposure or tonal balance.
- Lab-based enhancement offers a more scientifically grounded approach. By separating luminance from chromatic information, it enables precise saturation control with significantly lower risk of color deviation, ensuring greater color stability.
While both methods are powerful, they also face limitations — particularly when handling human skin tones and suppressing color noise in darker regions. To overcome these challenges, we’ve developed natural – saturation adjustment algorithms that provide a more natural and nuanced enhancement, resulting in a more pleasing visual output.
Super-Resolution — Transforming Resolution, Transforming Visuals
ZEGOCLOUD’s super-resolution technology enables real-time enhancement of low-resolution video by reconstructing high-resolution details lost during capture, compression, or transmission. The algorithm intelligently predicts and restores fine visual information, delivering significantly sharper and clearer output without increasing bandwidth usage.
This capability is designed specifically for real-time video applications, where both visual quality and system efficiency are critical.
Challenges of Conventional Super-Resolution Solutions
Most mainstream super-resolution models rely on heavy deep-learning architectures that impose significant performance overhead:
| Constraint | Typical Deep Learning Models |
|---|---|
| Model size | > 300,000 parameters |
| Computational cost | > 100 billion operations |
| Hardware requirement | High-performance GPU |
| Real-time capability | Limited |
| Mobile suitability | Poor |
For example, when upscaling video from 640×360 to 1280×720, these models frequently fail to maintain 30 FPS on standard GPUs, making them impractical for real-time communication and mobile environments.
ZEGOCLOUD’s Lightweight Super-Resolution Architecture
ZEGOCLOUD introduces a purpose-built super-resolution network optimized for real-time performance:
- Extremely low parameter count
- Minimal computational overhead
- Mobile-device friendly
- Real-time processing capability
This design allows high-quality super-resolution processing directly on mobile devices and edge platforms, without compromising frame rate, system stability, or battery efficiency.
Key Benefits for Developers and Platforms
- Real-time high-resolution video enhancement
- Smooth performance on mobile and low-power devices
- No additional bandwidth consumption
- Seamless integration with live streaming, video calling, and playback workflows
Whether used in live broadcasting, interactive video communication, or on-demand playback, ZEGOCLOUD’s super-resolution technology ensures consistently high visual quality across devices and network conditions.
Measuring What Matters: Quality Evaluation Framework
Ensuring the effectiveness of ZEGOCLOUD’s video algorithms requires a rigorous and multi-dimensional evaluation framework. We employ a combination of objective metrics and subjective human assessment to comprehensively measure image and video quality across different scenarios.
Our evaluation methods are divided into reference-based and no-reference approaches.
1. Reference-Based Evaluation
These methods compare the processed output with a known high-quality reference image or video.
PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio)
PSNR is one of the most widely used objective metrics for image and video quality assessment. It measures the ratio between the maximum possible signal power and the power of corrupting noise.
- Calculation steps:
- Compute the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between the processed image and the reference image
- Calculate the logarithmic ratio of the maximum pixel value squared to the MSE
- Interpretation:
- Higher PSNR indicates less distortion and better quality
- High-quality images typically fall within the 20–40 dB range
SSIM (Structural Similarity Index)
Unlike PSNR, SSIM evaluates similarity based on luminance, contrast, and structural information, making it more aligned with human visual perception.
- A fixed-size window (e.g., 8×8 pixels) slides across the image
- SSIM is calculated for each window and averaged to produce the final score
- Score range:
- 1.0 → perfect similarity
- 0.0 → no similarity
LPIPS (Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity)
LPIPS is a perceptual metric based on deep neural networks (such as VGG or AlexNet).
- Extracts high-level semantic features
- Measures the distance between feature representations of two images
- Lower LPIPS indicates closer alignment with human perception
- Particularly effective for complex visual content
2. No-Reference Evaluation
These methods evaluate image quality without requiring a reference image.
NIQE (Natural Image Quality Evaluator)
NIQE is a widely used no-reference quality metric based on statistical modeling of natural images.
- Processing steps:
- Convert image to grayscale
- Normalize contrast and resize
- Extract local features (e.g., gradients, textures) and global features (e.g., mean, variance, histogram)
- Compare feature distribution with a trained natural-image model
- Interpretation:
- Lower NIQE scores indicate better quality
- Best suited for general quality estimation, though less sensitive to high-frequency noise and complex distortions
MOS (Mean Opinion Score)
MOS provides a subjective quality assessment based on human perception.
- A group of evaluators score visual quality on a 1–5 scale
- Outliers are removed and the average is calculated
- Accurately reflects user perception, but:
- Resource-intensive
- Not suitable for real-time optimization or large-scale automated testing
By combining objective metrics (PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, NIQE) with subjective human feedback (MOS), we ensure continuous optimization of its image and video enhancement algorithms—achieving both technical excellence and superior perceived quality.
Real-World Business Impact
By integrating ZEGOCLOUD’s video algorithms, your company will achieve:
- Higher viewer engagement and session duration
- Reduced user churn caused by visual frustration
- Improved brand perception through premium video experiences
- Stable real-time video quality across devices and networks
From live streaming and social platforms to video conferencing, education, and telemedicine, ZEGOCLOUD provides the visual foundation for next-generation applications.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, delivering consistent real-time video quality is essential across live streaming, social platforms, education, and enterprise communication. ZEGOCLOUD’s video algorithms and real-time technologies address core challenges — from low latency and adaptive enhancement to cross-device stability — enabling reliable, high-quality experiences. By focusing on end-to-end performance,we support the industry’s shift toward more immersive and interactive video applications.
Whether you are an enterprise or an individual developer, come to explore how these solutions can enhance your platform’s video experience, visit ZEGOCLOUD or start testing the SDKs today.
Let’s Build APP Together
Start building with real-time video, voice & chat SDK for apps today!










