By Poor Network
Troubleshooting and analysis: The lag is caused by poor network on the streaming end (viewer)
Overview
Lagging is one of the most common abnormal experiences in audio and video calls, mainly occurring on the playback side (viewers). Since there are many possible causes for lag, this article describes how to use Analytics Dashboard to determine whether lag during a user's call is caused by poor network on the playback side (viewer).
Troubleshooting Steps
Before troubleshooting the cause of lag, please refer to Call Quality Monitoring to familiarize yourself with the features of the Analytics Dashboard - Call Quality Monitoring module.
1 Locate the Target Stream
-
Obtain relevant information about the lag call as much as possible, including: the playback user ID, stream ID, call start time, and call end time.
-
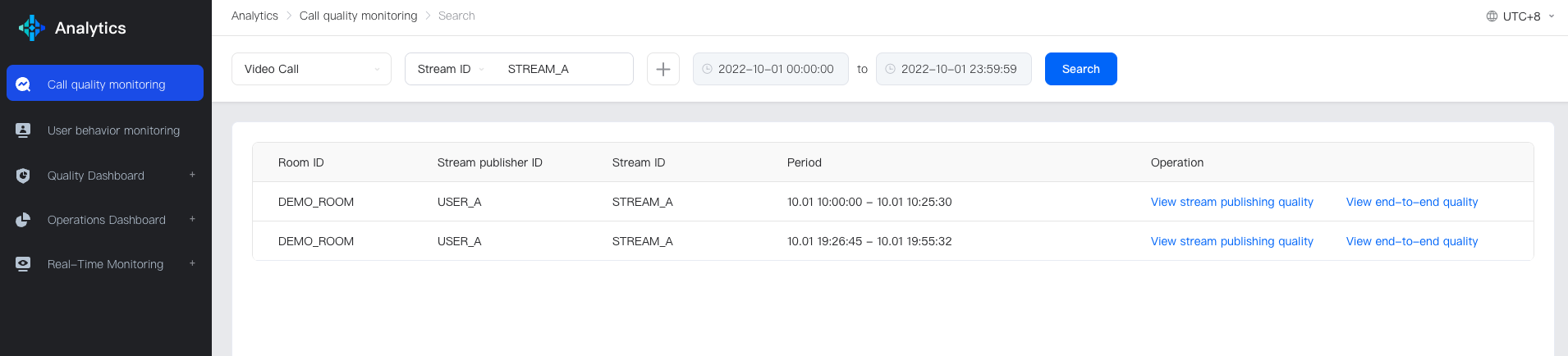
Enter the Search Page of Call Quality Monitoring, locate the target stream, select the target App, input the playback user ID or stream ID, and call time, and retrieve the stream list information.
The following figure shows an example of the search result using the stream ID:
2 Analyze Whether the Lag is a User-Specific Case
After users report a lag issue, developers need to analyze whether the problem is a user-specific case or a general issue. To confirm whether the lag is a user-specific case, developers can compare the bitrate data of the problem user with that of other playback users on the Publish Quality Page: Prism
-
If only this user lags at this moment when pulling, and other users do not lag at the same time, it can be determined that the lag is a user-specific case, as shown in the following figure:

-
If the bitrate chart of all playback users appears to lag at the same time, and the received bitrate also has similar fluctuations, and the transmitted bitrate of the streaming user also has similar fluctuations, the cause of the lag may be due to the quality fluctuation on the streaming side. At this moment, all playback users lag, which is a general issue, and the cause needs to be further investigated. The following figure shows the bitrate and lag rate of the common lag problem:
Bitrate and Lag Rate of Common Lag Problem
3 Determine Whether the Lag is Caused by Poor Network on the Streaming End (Viewer)
After confirming that the lag is a user-specific case, enter the End-to-End Details Page, and analyze whether the lag is caused by poor network on the streaming end (viewer). The analysis and troubleshooting steps are as follows:
-
Check whether the received bitrate and frame rate of the playback device (viewer) are normal to determine whether the audio and video data transmission is normal.
-
During the lag period, the received bitrate and frame rate data fluctuate abnormally, indicating that the receiving end receives audio and video data abnormally, and the cause of the data transmission abnormality needs to be further investigated. The following figure shows the abnormal frame rate and bitrate of the receiving end:

-
During the lag period, the received bitrate and frame rate data are normal, the received value is similar to the transmitted value, and the expected value is met, indicating that the audio and video data transmission is normal, and the lag is probably caused by other reasons. The following figure shows the normal bitrate and frame rate of the receiving end:
Normal Bitrate and Frame Rate of the Receiving End
-
-
Confirm that the received bitrate and frame rate data transmission is abnormal, and investigate and analyze the cause of the abnormal data transmission.
There may be the following three reasons:
-
Whether it is caused by the special behavior of the user?
For example, the user closes/opens the network before and after the frame rate and bitrate change, causing the network state to change, which can be viewed through the user behavior axis to check whether there is a special user behavior at the corresponding moment.
-
Whether it is caused by the change of configuration?
By checking the configuration table, it can be confirmed whether there are some configuration changes before and after the frame rate and bitrate change, causing the frame rate and bitrate changes.
-
Whether it is caused by network exception?
Check whether the end-to-end delay and end-to-end packet loss rate fluctuate abnormally during the frame rate and bitrate change period, and confirm whether there is an exception in the network during the data transmission process.
-
The end-to-end delay and end-to-end packet loss rate do not fluctuate abnormally, the delay value fluctuates in a small range near a specific value, the packet loss tends to 0, the data curve shows a small fluctuation trend, the chart curve shows smooth and stable performance, it can be determined that the network link is normal, as shown in the following figure:
Normal Network Link
-
The end-to-end delay data shows a sudden change (such as a sharp increase), the curve has a prominent region, the packet loss data increases abnormally, the chart curve shows obvious fluctuations, it can be determined that the network link is abnormal, as shown in the following figure:

-
-
-
Confirm that the lag is caused by network exception, check the downstream delay and downstream packet loss, and further confirm whether the network exception occurs in the viewer's downstream network.
-
If the downstream delay value fluctuates obviously, the downstream packet loss rate data increases sharply, the data curve shows obvious fluctuations, it can be determined that the downstream network of the user is abnormal at the time of lag, as shown in the following figure:

-
If the downstream delay fluctuates in a small range near a specific value, the curve does not show a sharp increase, the packet loss data tends to 0, it can be determined that the downstream network of the user is normal at the time of lag, it may be the network exception problem of other transmission stages, as shown in the following figure:
Normal Downstream Network
-
Solution
By the above troubleshooting steps, if you determine that the lag is caused by the abnormal downstream network of the viewer, you can guide users to solve the problem through the following methods:
- Switch to a better network.
- Move the device closer to the Wi-Fi router.
- If the user is outdoors, they can go to a more open area to get better mobile network.
- Other methods to improve network quality.
