By Resources Overload
Troubleshooting and analysis: The lagging is caused by insufficient CPU or memory resources of the streaming device (viewer).
Overview
Lagging is one of the most common abnormal experiences in audio and video calls, mainly occurring on the playback side (viewers). Since there are many possible causes for lag, this article describes how to use Analytics Dashboard to determine whether lag during a user's call is caused by insufficient CPU or memory resources on the playback device (viewer).
Troubleshooting Steps
Before troubleshooting the cause of lag, please refer to Call Quality Monitoring to familiarize yourself with the features of the Analytics Dashboard - Call Quality Monitoring module.
1 Locate the Target Stream
-
Obtain relevant information about the lag call as much as possible, including: the playback user ID, stream ID, call start time, and call end time.
-
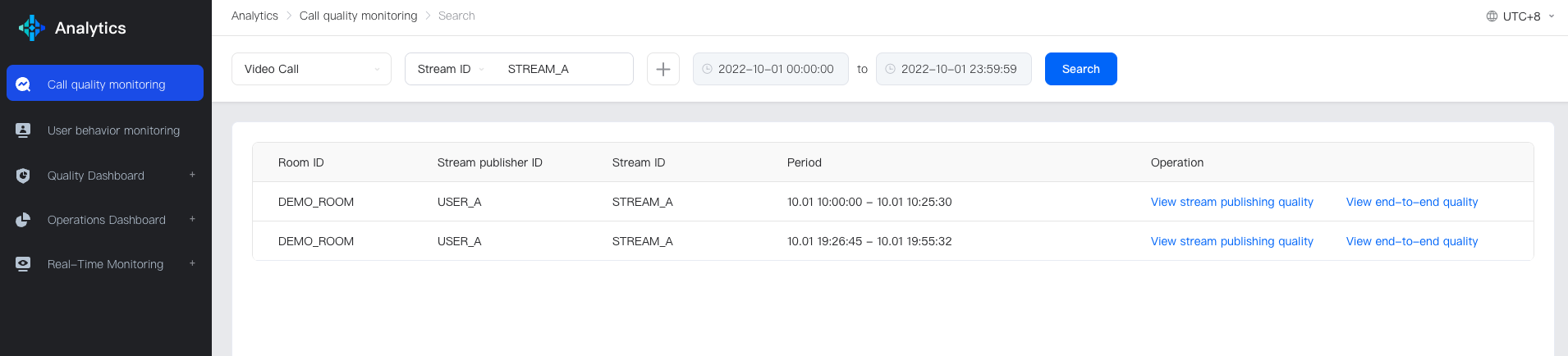
Enter the Search Page of Call Quality Monitoring, locate the target stream, select the target App, input the playback user ID or stream ID, and call time, and retrieve the stream list information.
The following figure shows an example of the search result using the stream ID:
2 Analyze Whether the Lag is a User-Specific Case
After users report a lag issue, developers need to analyze whether the problem is a user-specific case or a general issue. To confirm whether the lag is a user-specific case, developers can compare the bitrate data of the problem user with that of other playback users on the Publish Quality Page: Prism
-
If only this user lags at this moment when pulling, and other users do not lag at the same time, it can be determined that the lag is a user-specific case, as shown in the following figure:
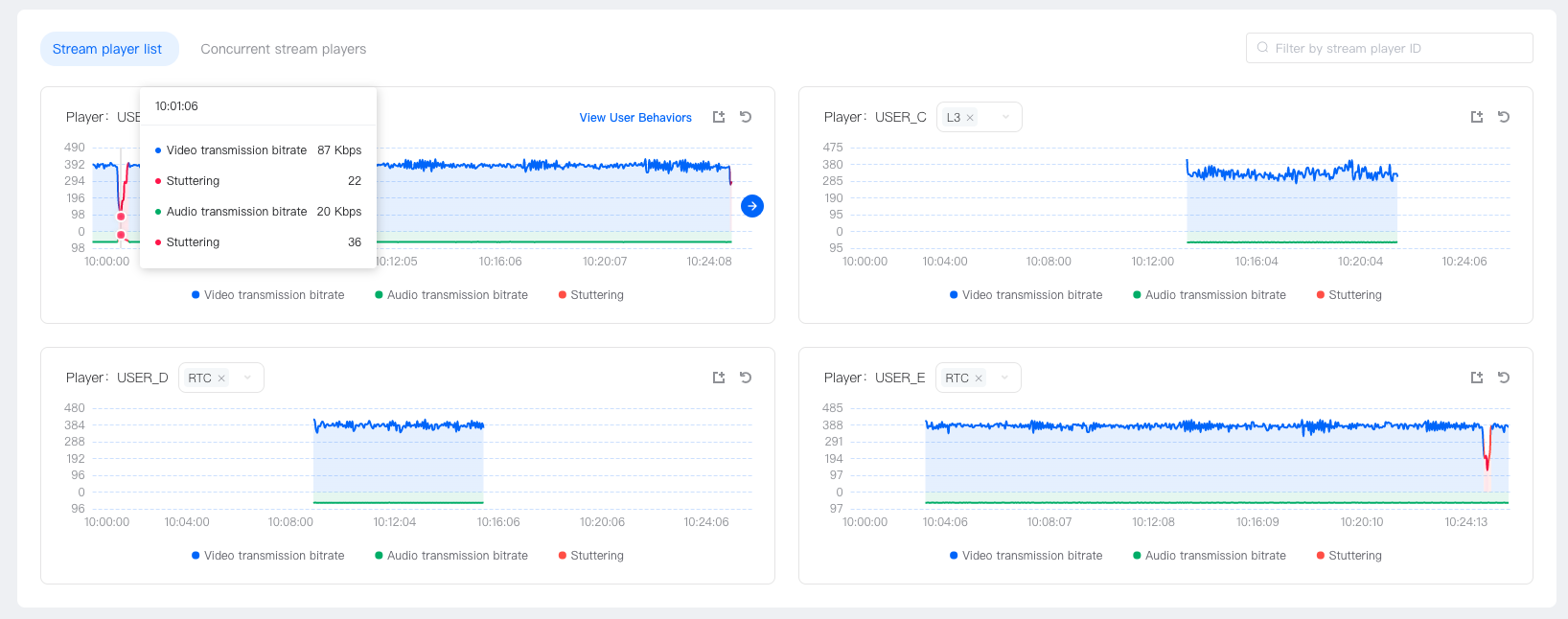
-
If the bitrate chart of all playback users appears to lag at the same time, and the received bitrate also has similar fluctuations, and the transmitted bitrate of the streaming user also has similar fluctuations, the cause of the lag may be due to the quality fluctuation on the streaming side. At this moment, all playback users lag, which is a general issue, and the cause needs to be further investigated. The following figure shows the bitrate and lag rate of the common lag problem:
Bitrate and Lag Rate of Common Lag Problem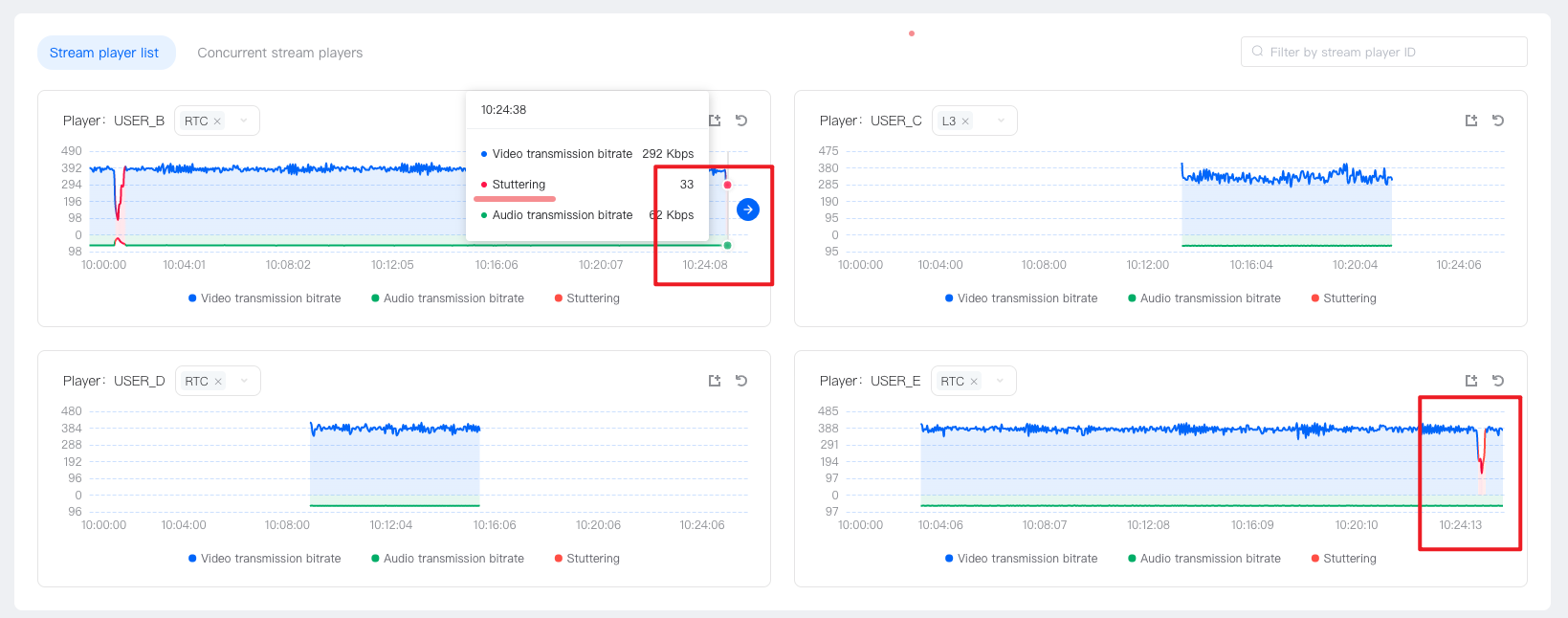
3 Determine Whether the Lag is Caused by Insufficient CPU or Memory Resources of the Playback Device (Viewer)
After confirming that the lag is a user-specific case, enter the End-to-End Details Page, and analyze whether the lag is caused by insufficient CPU or memory resources of the playback device (viewer). The analysis and troubleshooting steps are as follows:
-
Check whether the received bitrate and frame rate of the playback device (viewer) are normal to determine whether the audio and video data transmission is normal.
-
During the lag period, the received bitrate and frame rate data fluctuate abnormally, indicating that the receiving end receives audio and video data abnormally, and the cause of the data transmission abnormality needs to be further investigated. The following figure shows the abnormal frame rate and bitrate of the receiving end:
Abnormal Frame Rate and Bitrate of the Receiving End
-
During the lag period, the received bitrate and frame rate data are normal, the received value is similar to the transmitted value, and the expected value is met, indicating that the audio and video data transmission is normal, and the lag is probably caused by local rendering exception. The following figure shows the normal bitrate and frame rate of the receiving end:

-
-
Confirm that the audio and video bitrate data received by the SDK is normal, then the lag is probably caused by rendering exception. You can analyze and confirm whether the user device has insufficient resources to render audio and video normally when rendering audio and video, causing lag, through the following methods:
-
Check whether the
CPU usageof the playback device (viewer) is normal during the lag period to determine whether the audio and video data transmission is normal.- If the
CPU usageof the playback device (viewer) is high during the lag period (above 80%), it can be initially determined that the rendering exception is caused by the highCPU usage, which cannot render audio and video normally, as shown in the following figure:
- If the
CPU usageof the playback device (viewer) is normal during the lag period, it can be determined that the rendering exception is not caused by the insufficientCPU resources, and the cause of the rendering exception needs to be further investigated.
- If the
-
Check whether the
memory usageof the playback device (viewer) is normal during the lag period to determine whether the audio and video data transmission is normal.-
Compare the
memory totaland the currentsystem memory usagedata. If thesystem memory usagecurve is at a high level and close to the memory total, it indicates that the system memory resources are insufficient, which may cause audio and video rendering exceptions and cause lag. The following figure shows the abnormal memory usage of the playback device (viewer):
-
If the current
system memory usageis low, it indicates that the memory resources are sufficient, and it can be determined that the cause of the lag is not related to the memory usage.
-
-
4 Solution
By the above troubleshooting steps, if you determine that the lag may be caused by insufficient device resources, you can guide users to solve the problem through the following methods:
- Close some unnecessary software to release CPU resources and observe whether the lag can be improved.
- Delete some unnecessary files to release memory resources and observe whether the lag can be improved.
- Restart the App or device and observe whether the lag can be improved.
- Other methods to improve the use of device resources.
