Interact with AI in IM and make voice calls
This document is designed to guide developers on how to leverage the real-time communication capabilities of ZIM (ZEGOCLOUD In-app chat) combined with the natural language processing capabilities of LLM to implement In-app Chat with AI and initiate voice calls using AI Agent functionality.
Core Concepts
Before diving into implementation details, let's clarify several core concepts:
- ZIM (ZEGOCLOUD In-app chat): ZEGOCLOUD's in-app chat service. It supports various message types including text, images, and files, with room management and user status notification capabilities, providing a solid foundation for in-app interactions.
- Large Language Model (LLM): A deep learning model trained on massive text datasets. LLMs can understand and generate natural language text, widely used in Q&A systems, intelligent conversations, text creation, and various other scenarios.
- In-app Chat: Users interact with LLM through text input via ZIM service.
- Voice Call: Users enter RTC rooms through AI Agent service to have voice conversations with AI.
Implementation Architecture for In and Voice Calls
This is the architecture for implementing both In-app Chat and voice calls with AI in one APP.
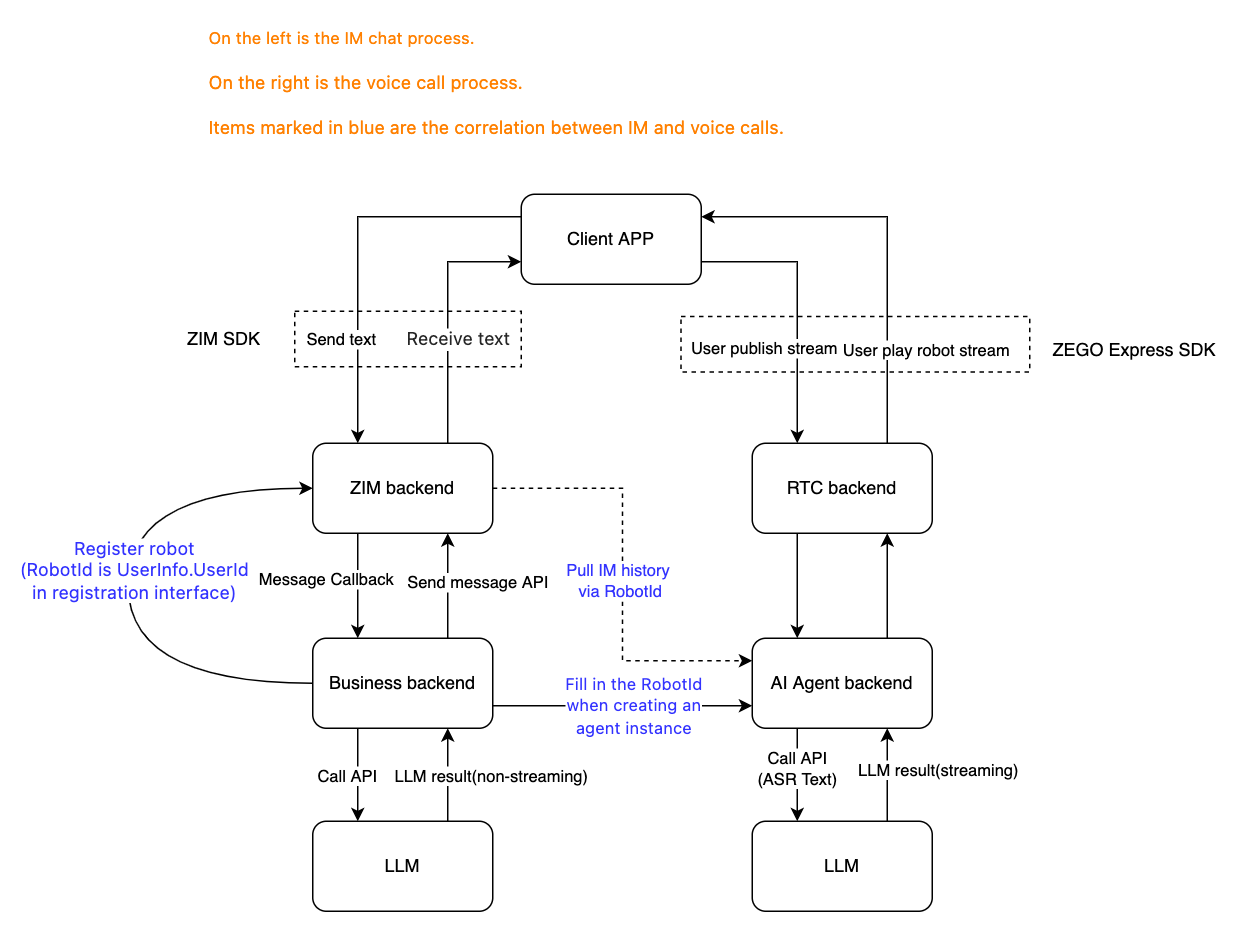
In-app Chat
- Client APP: Integrates ZIM SDK to implement text message sending/receiving and persistent chat history storage.
- ZIM Backend: Receives and processes messages from clients. Safely and reliably delivers user messages to business backend through message callbacks.
- Business Backend: Serves as the core processing hub, responsible for:
- Calling ZIM backend API to register a bot. The bot's
UserIdwill be used asRobotIdfor loading historical messages during voice calls. - Receiving user messages from ZIM, preprocessing messages including sensitive word filtering and preliminary intent recognition.
- Calling LLM service to send processed user messages to LLM for deep analysis and content generation.
- After receiving LLM response content, post-processing the reply including format output and secondary content safety verification.
- Calling ZIM backend API to send replies back to clients as the bot through ZIM.
- Calling ZIM backend API to register a bot. The bot's
Voice Call
- Client APP: Integrates ZEGO Express SDK to implement voice call functionality.
- Business Backend: Calls the create agent instance API and passes the bot's
UserIdas theRobotIdparameter to AI Agent service. - AI Agent Backend: Based on the
RobotIdpassed from business backend, loads historical messages from ZIM backend as input context for the agent. The LLM configured for the agent will use this context as chat history to interact with users in voice calls and answer user questions.
Sample Code
The following are client sample codes for integrating ZIM SDK to implement In-app Chat and business backend sample codes for integrating ZIM and real-time interactive AI Agent APIs. You can refer to these samples to implement your own business logic.
Includes basic capabilities such as login, sending/receiving text messages, publishing stream, playing stream, and leaving room.
Includes basic capabilities such as login, sending/receiving text messages, publishing stream, playing stream, and leaving room.
Includes basic capabilities such as login, sending/receiving text messages, publishing stream, playing stream, and leaving room.
Includes basic capabilities such as login, sending/receiving text messages, publishing stream, playing stream, and leaving room.
Includes basic capabilities such as obtaining ZEGOCLOUD Token, registering ZIM bots, registering agents, creating agent instances, and deleting agent instances.
Quick Implementation of In-app Chat with AI
1. Set Up Business Backend
The business backend serves as a bridge connecting ZIM and LLM. You can use any backend technology stack you're familiar with, such as Node.js, Python, Java, Go, etc.
1.1 Register ZIM Bot
In-app Chat and AI Agent service need to receive and send messages through ZIM bots. Therefore, you need to specify a bot UserId (i.e., RobotId) and call ZIM backend API to register a bot.
For detailed registration instructions, please refer to ZIM Bot Registration Instructions.
1.2 Set Up ZIM Callbacks to Receive User Messages
Configure ZIM backend to notify your business backend of message events through callback mechanisms. For detailed configuration instructions, please refer to ZIM Callback Configuration Instructions.
Your business backend needs to implement an HTTP interface to listen for Message Sent Callbacks. Here's sample callback data:
{
"appid": "1",
"event": "send_msg",
"nonce": "350176",
"signature": "signature",
"timestamp": 1679553625,
"from_user_id": "user_id_1",
"conv_type": 0,
"conv_id": "@RBT#AIAgentExample1",
"msg_type": 1,
"msg_body": "msg_body",
"msg_id": "857639062792568832",
"payload": "payload",
"msg_time": 1679554146000,
"send_result": 0,
"sub_msg_type": 0,
"user_list":[
]
}1.3 Call LLM Service to Generate AI Replies
After receiving user messages from callbacks, the business backend needs to call LLM service to generate AI replies. You can use LLM services provided by third-party service providers such as DeepSeek, Volcano Ark (DouBao), MiniMax, Volcano Engine, Alibaba Cloud, StepFun, OpenAI (GPT series), or self-deployed LLM services.
Please refer to the relevant service provider's API documentation for integration. Here's sample code for calling DeepSeek model using Node.js:
async function generateLLMResponse(messages: MessageItem[]): Promise<string> {
try {
console.log('Preparing to generate LLM response, message context:', messages);
// Get LLM configuration from environment variables
const apiKey = process.env.LLM_API_KEY;
const baseURL = process.env.LLM_BASE_URL;
const model = process.env.LLM_MODEL || 'deepseek-v3-250324';
if (!apiKey || !baseURL) {
console.error('Missing LLM configuration, please check environment variables');
return "Sorry, I'm temporarily unable to reply to your message. Please try again later.";
}
// Convert message format
const formattedMessages = messages.map(msg => ({
role: msg.role as "user" | "assistant" | "system",
content: msg.content
}));
// Add system prompt
formattedMessages.unshift({
role: "system",
content: "You are a helpful assistant. Please answer user questions concisely and clearly."
});
// Use fetch API to call LLM service. Note: using non-streaming response.
// !mark(1:11)
const response = await fetch(baseURL, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': `Bearer ${apiKey}`
},
body: JSON.stringify({
messages: formattedMessages,
model: model
})
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`LLM API request failed: ${response.status} ${response.statusText}`);
}
const data = await response.json();
// Get reply content
const reply = data.choices?.[0]?.message?.content || "Sorry, I cannot generate a reply.";
return reply;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error generating LLM response:', error);
return "Sorry, there was an issue processing your request. Please try again later.";
}
}1.4 Send AI Reply Back to Client via ZIM
After obtaining the LLM reply, the business backend needs to use ZIM backend API to send this reply content to the real user as AI.
For specific API usage, please refer to the Send Peer Message interface in ZIM backend API documentation.
Here's an example of sending messages through ZIM backend API using Node.js:
async function sendReplyMessage(fromUserId: string, toUserId: string, message: string) {
try {
// Build message body
const messageBody = {
Message: message, // LLM reply content
ExtendedData: ''
};
// Send message
// ZegoZIM.getInstance().sendPeerMessage is a demo wrapper method. For complete implementation, refer to: https://github.com/ZEGOCLOUD/ai_agent_quick_start_server/blob/im_and_voice/src/lib/zego/zim.ts#L162
// Please refer to detailed send peer message API documentation: https://www.zegocloud.com/docs/zim-server/messaging/send-a-one-to-one-message
const result = await ZegoZIM.getInstance().sendPeerMessage(
// !mark(1:2)
fromUserId, // Sender ID, i.e., UserInfo.UserId from bot registration (Bot ID)
[toUserId], // Receiver ID array (Real user ID)
ZegoMessageType.Text, // Message type: Text
messageBody, // Message content
ZegoMessagePriority.Medium // Message priority: Medium
);
console.log('Send reply message result:', result);
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error sending reply message:', error);
throw error;
}
}2. Client Processing Logic
The client's ZIM SDK will listen for and receive AI reply messages from the business backend (forwarded through ZIM backend). You need to implement message receiving logic on the client side and display the content in the user interface.
Prerequisites
Please integrate ZIM SDK in your client APP. Refer to integration guides for each platform:
2.1 Get Historical Messages from AI Conversations
When entering the AI chat page, you need to retrieve historical messages from ZIM service. Here are sample codes for implementing historical message retrieval on each platform:
ZIMMessageQueryConfig queryConfig = new ZIMMessageQueryConfig();
queryConfig.count = 100; // Query count
queryConfig.reverse = true; // Query the latest count messages
// !mark(1:2)
String conversationId ; // Conversation ID for querying historical messages. i.e., bot `UserId` (i.e., RobotId)
ZIM.getInstance().queryHistoryMessage(conversationId, ZIMConversationType.PEER, queryConfig,new ZIMMessageQueriedCallback() {
@Override
public void onMessageQueried(String conversationID, ZIMConversationType conversationType,ArrayList<ZIMMessage> messageList, ZIMError errorInfo) {
if (errorInfo.code == ZIMErrorCode.SUCCESS) {
// Success
} else {
// Failure
}
}
});2.2 Send Messages to AI
After users input messages on the client, you can use ZIM SDK to send messages to AI. Here are sample codes for implementing message sending on each platform:
String text ; // Chat text
// !mark
String conversationId ; // Conversation ID for sending messages. i.e., bot `UserId` (i.e., RobotId)
ZIMTextMessage zimMessage = new ZIMTextMessage();
zimMessage.message = text;
// In peer chat scenario, set ZIMConversationType to PEER
// !mark
ZIM.getInstance().sendMessage(zimMessage, conversationId, ZIMConversationType.PEER, new ZIMMessageSendConfig(),
new ZIMMessageSentFullCallback() {
@Override
public void onMessageAttached(ZIMMessage message) {
// Insert message to list when sending starts
}
@Override
public void onMessageSent(ZIMMessage message, ZIMError errorInfo) {
// Send success
}
@Override
public void onMediaUploadingProgress(ZIMMediaMessage message, long currentFileSize,
long totalFileSize) {
}
@Override
public void onMultipleMediaUploadingProgress(ZIMMultipleMessage message, long currentFileSize,
long totalFileSize, int messageInfoIndex, long currentIndexFileSize, long totalIndexFileSize) {
}
});2.3 Receive AI Reply Messages
AI reply messages will be sent to the client through ZIM service via the business backend. You need to implement message receiving logic on the client side and display the content in the user interface. Here are sample codes for implementing message receiving on each platform:
ZIM.getInstance().setEventHandler(new ZIMEventHandler() {
@Override
// !mark
public void onPeerMessageReceived(ZIM zim, ArrayList<ZIMMessage> messageList, ZIMMessageReceivedInfo info,String fromUserID) {
// Only add messages from this conversation to this page
List<ZIMMessage> collect = messageList.stream()
.filter(zimMessage -> Objects.equals(Constant.agent_zim_robotid, zimMessage.getConversationID()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
});Asynchronous Processing and User Feedback
To avoid UI freezing or unresponsiveness due to lengthy LLM processing time, you can use the following methods to optimize interaction:
- After the client sends a message, you can immediately display "AI is thinking..." or similar waiting prompts in the interface.
- After the business backend receives user messages, it can quickly respond to the client that the message has been received, then asynchronously call LLM service. When LLM returns results, push the actual reply to the client through ZIM to update the interface.
Quick Implementation of Voice Calls with AI
In real application scenarios, users may switch between text and voice interactions. To maintain conversation continuity and context integrity, please refer to the following instructions to implement the association between In-app Chat historical messages and voice call messages.
Associate In-app Chat Historical Messages to Voice Calls
Before starting a call, you can associate In-app Chat historical messages to voice calls in the following way:
When creating an agent instance, configure the MessageHistory parameter:
- Set
MessageHistory.SyncMode(message sync mode) to0, indicating synchronization from ZIM historical messages - Provide complete ZIM-related information in
MessageHistory.ZIM, including:RobotId: The UserInfo.UserId corresponding to the ZIM bot registration API callLoadMessageCount: When creating agent instance, how many messages to fetch from ZIM service as context. Defaults to WindowSize value (upper limit).
After completing the above configuration, the created agent instance will automatically retrieve In-app Chat historical messages as LLM historical message input during voice interactions.
Associate Voice Call Context to In-app Chat
After the call ends, all voice call messages will be synchronized to ZIM service. You can synchronize these messages to In-app Chat after the call ends to maintain conversation continuity and context integrity.
For detailed steps, refer to the Get Historical Messages from AI Conversations section.
